|
MEPARTRICIN |
| Ipertrofan; Mepartricin; Mepartricina; Mepartricine; Mepartricinum; Methylpartricin; Orofungin; Tricandil; Tricangine; Partricin methyl ester; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
11121-32-7, 12795-77-6 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
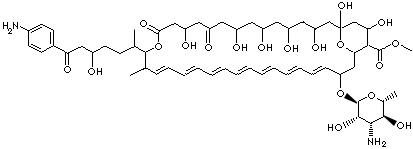
C60H88N2O19 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
1141.34 |
|
H.S. CODE |
2941.90.1010 |
|
ACUTE TOXICITY |
LD50 Oral - mouse: > 2,000 mg/kg |
|
SMILES |
C12(OC(C(C(C1)O)C(=O)OC)C(OC1[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O1)C) O)N)O)CC=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC(C(OC(=O)CC(CC(=O)CC(CC(CC(C C(C2)O)O)O)O)O)C(CCC(CC(=O)c1ccc |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antibacterial agent, Anti-Infective agent, Antifungal, Antiparasitic, Antiprotozoal |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Mepartricin is used in studies on sterol biosynthesis and bacterial cell
membranes. It may be incorporated into liposomes. |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
slightly yellow powder. |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBILITIES |
|
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
|
| POLYMERIZATION |
|
| NFPA RATING | Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Instability: 0; |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL |
|
|
|
|
POTENTIAL HEALTH EFFECTS |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
No known OSHA hazards |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May cause irritation of the digestive tract. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
| TARGET ORGANS |
No data found. |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||||||||
|
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ Polyene macrolides:Polyene macrolides have historically been the first antibiotics used in antifungal therapy. The discovery of nystatin and amphotericin in 1950s provided new opportunities for treatment of various fungal infections. Later, more than 200 other polyene macrolides with antifungal activity have been discovered, although only amphotericin B and nystatin have found substantial use , nystatin, candicidin, pimaricin, methyl partricin and trichomycin are currently being used in human therapy. In general, the polyene macrolides are rather toxic, and may cause such serious side-effects as renal tubular damage and thrombophlebitis, especially upon intravenous administration. Despite of that, broad spectrum of activity and low frequency of appearance of resistant pathogens make polyene antibiotics, like amphotericin B, the drug of choice when dealing with life-threatening systemic fungal infections. Polyene antibiotics display a unique mode of action by making the fungal cell membranes permeable to ions and other small molecules via polyene-ergosterol interactions.
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to light yellow crystalline powder |
|
CONTENT |
95% min |
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|