|
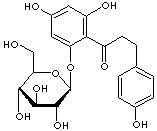
PHLORHIZIN |
| Synonyms. Phlorhizin; Isosalipurposide; Phloretin 2'-glucoside; Phloretin-2'-O-beta-glucoside; Phloridzin; Phlorizin; Phlorizoside; 2'-(beta-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-4',6'-dihydroxy-3- (4-hydroxyphenyl) propiophenone; 1-(2-(beta-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-4,6-dihydroxyphenyl)-3- (4-hydroxyphenyl)- 1-propanone; Phloretin 2'-beta-D-glucopyranoside; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | |
|
CAS RN |
60-81-1 (Anhydrous), 7061-54-3 (hydrate) |
|
EINECS RN |
200-487-1 |
|
FORMULA |
C21H24O10·2H2O |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
472.44 |
|
H.S CODE |
2938.90.0000 |
|
SMILES |
c1(c(O[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H]([C@H]2O)O)CO)cc(O) cc1O)C(CCc1ccc(O)cc1)=O |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Dihydrochalcone glycoside, Flavonoid |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Other RN: 112318-65-7, 16055-86-0, 52276-56-9 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
White to yellowish powder |
MELTING POINT |
106 ~ 110 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
0.72 |
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pKa |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 0, Flammability:0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking - Phlorizin Google Scholar Search - Phlorhizin Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Phlorhizin PubChem Compound Summary - Phlorhizin Drug Bank - Phlorhizin KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Phlorhizin http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Phlorhizin http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Phlorhizin http://www.mdpi.com/ Among the phenolic compounds, phloretin and its glycosylated derivative, phloridzin, are typical of apple and the other fruit of the Rosaceae family. In particular, phloridzin is found in large amount in the pips, but it is also present in apple juice and skin. Phloridzin has antioxidant activity allowing a cardiovascular protection similar to that of estrogens. Moreover, phloridzin is capable of acting on melanogenesis by activating a cascade of enzymes including tyrosinase, thus allowing increased protection against ultraviolet radiation. Phloridzin also has antidiabetic action by competitive inhibition of the sodium-dependent blood transport of metabolites such as glucose, galactose and the like. Phloridzin is also involved in inhibiting the growth of tumor cells by blocking the activity of protein kinase C. |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |
|
APPEARANCE |
White to yellowish powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
-50º ~ -54º (c = 3 in ethanol) |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
5.0% max |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|
As |
1ppm max |
|
Pb |
3ppm max |
|
MICROBIOLOGICAL TEST |
Total Plate Count: 1000 organisms/g max |
|
PARTICLE SIZE |
100 mesh |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION | |
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION | |
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation. |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Warning |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H315-H319-H335 |
|
P STATEMENTS |
P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
36/37/38 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-36 |
|
|