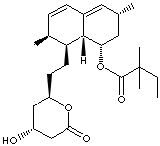
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
Anticholesteremic, Antihyperlipidemic, Antilipemic, Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor, Hypolipidemic, Lipid Regulator
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
Health: 1, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Simvastatin
PubChem Compound Summary - Simvastatin
Drug Bank - Simvastatin
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Simvastatin
http://www.hcc.bcu.ac.uk/
The
beneficial effects of statins are the result of their capacity to
reduce cholesterol biosyntesis, mainly in the liver, where they
are selectively distributed, as well as to the modulation of lipid
metabolism, derived from their effect of inhibition upon HMG-CoA
reductase. Statins have antiatherosclerotic effects, that positively
correlate with the percent decrease in LDL cholesterol. In addition,
they can exert antiatherosclerotic effects independently of their
hypolipidemic action. Because the mevalonate metabolism generates
a series of isoprenoids vital for different cellular functions,
from cholesterol synthesis to the control of cell growth and differentiation,
HMG-CoA reductase inhibition has beneficial pleiotropic effects.
Consequently, statins reduce significantly the incidence of coronary
events, both in primary and secondary prevention, being the most
efficient hypolipidemic compounds that have reduced the rate of
mortality in coronary patients. Independent of their hypolipidemic
properties, statins interfere with events involved in bone formation
and impede tumor cell growth.
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
Simvastatin, a synthetic analog of lovastatin, is a specific inhibitor of
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase.) HMG-CoA is a
major therapeutic target for reduction of low density lipoprotein (LDL)
cholesterol. Simvastatin may also have beneficial effects on endothelial
function, smooth muscle cell function, hemostasis, vascular wall function, LDL
oxidation, and inflammation. Simvastatin can be activated prior to use by
treatment with NaOH in EtOH.
Simvastatin is a specific inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early step in cholesterol biosynthesis. It is used in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia, as it reduces levels of low-density lipoproteins and triglycerides, and raises high-density lipoprotein levels. Simvastatin is a lactone that is readily hydrolyzed in vivo to the corresponding β-hydroxyacid, and can be activated prior to use with NaOH in EtOH treatment. It is a synthetic analog of lovastatin (Cat. No. M2147).
Local
statins (or hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors)
|
Statin |
CAS RN. |
|
Mevastatin |
73573-88-3 |
| Lovastatin | 75330-75-5 |
| Simvastatin | 79902-63-9 |
| Pravastatin | 81093-37-0 |
| Fluvastatin | 93957-54-1 |
| Fluvastatin Sodium | 93957-55-2 |
| Atorvastatin | 134523-00-5 |
| Atorvastatin Calcium | 134523-03-8 |
| Cerivastatin Sodium | 143201-11-0 |
| Cerivastatin | 145599-86-6 |
| Pitavastatin | 147511-69-1 |
| Rosuvastatin | 287714-41-4 |
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
MELTING POINT
134 - 136 C
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
IMPURITY
Total
impurity: 0.5%
max
Individual Impurity: 0.2% max
0.2% max
Hazard OVERVIEW
Not known
GHS
PICTOGRAMS
None
HAZARD STATEMENTS
H303 May be harmful if swallowed.
SAFETY PHRASES
22 -24/25