PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
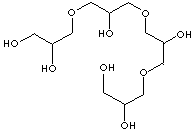
C12H26O9
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
An emulsion is a mixture of two repel substances (water and oil).It induces a dispersion of undissolved material throughout a liquid. The dispersed phase is dispersed in the other continuous phase. Emulsions are unstable and thus tend to revert to the stable state of oil separated from water spontaneously. Physical energy such as shaking, stirring, homogenizers, or spray processes is needed to keep an emulsion. Surfactants increase the kinetic stability of emulsions and make the emulsion does not change significantly for long term. An emulsifier is a type of surfactant used to keep emulsion stable and well dispersed. Emulsifiers typically have a hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail in one molecule. The emulsifiers will surround an hydrophobic molecule and hydrophilic tail form a protective layer so that the oil molecules cannot "clump" together. This action helps keeps phase well dispersed. Some of the most important emulsifiers include salts or esters of higher fatty acids, fatty alcohols, esters of monoglycerides, gelatin, lecithins, polysaccharides and casein.
Glycerides (also known as acylglycerols) are esterified to glycerol with fatty acids. Glycerol haing three hydroxyl functional groups is esterified with one, two or three fatty acids to form monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides respectively. A monolyceride is a compound consisting of one fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkage. Diglyceride and triglyceride consists of two and three fatty acid chains respectively. Examples of triglyceride include triacetin, trimyristin, and triolein. Monoglyceride usually occurs as an intermediate in triglyceride metabolism by means of a release of a fatty acid from lipase. The commercial source may be either animal or vegetable fats, and synthetically produced as well. Mono- and diglycerides are common food additives used as an emulsifier or stabilizer to blend together certain ingredients of oil-hating and water-hating, which would not otherwise blend well. .
Either the primary hydroxyl or the secondary hydroxyl groups in glycerol can condense to form polyglycerols (hydroxy-containing ethers). The simplest example is diglycerol. Diglycerol, Triglycerol, Tetraglycerol, Pentaglycerol, Hexaglycerol, Heptaglycerol, Octaglycerol, Nonaglycerol, Decaglycerol indicate 2 - 10 degrees of polymerization respectively. The primary hydroxyls are involved in linear polymerization, whereas the secondary hydroxyl groups are in branched polymer formation. If the polymerization proceeds to tri-, tetra- and higher glycerols the number of isomers increases exponentially. Polyglycerol esters are mixtures of the esters of fatty acids with the polyglycerol mixture. They are formed by an alkaline catalyzed random polymerization of glycerol followed by an esterification with isolated fatty acids. Typically 30 - 50 % of the total amount of hydroxyl groups are esterified by fatty acids. The polyglycerol mixture varies in the degree of polymerization, types and positions of esterified fatty acids, which provide wide range of hydrophilicity and lipophilicity (HLB ranges from 3 to 13). This range provide a variety of choice for the end applications. Polyglyceryl esters are important emulsifier in cosmetic, in food, pharmaceutical and other industries. Their amphiphilic character enables their use as a stabilizer for various suspensions. They are used as an emulsifier, viscosity controler, dispersant and stabilizer for the final products.| polyglycerols or esters |
CAS RN. |
|
1,3-Dioctadecanoylglycerol |
504-40-5 |
| Cytidine diphosphodiglyceride-serine Ophophatidyl transferase | 9068-48-8 |
| Diglyceryl stearate | 12694-22-3 |
| Tetranitro diglycerin | 20600-96-8 |
| Diglyceryl monooleate | 49553-76-6 |
| Dimyristoyl diglyceride | 53563-63-6 |
| Diglycerindiformal | 56552-15-9 |
| Diglycerin | 59113-36-9 |
| Polyoxyethylene glycerides | 61163-33-5 |
| Mono- and diglycerides | 67254-73-3 |
| Hydrogenated mono- and diglycerides | 67784-87-6 |
| Diglyceryl diisostearate | 67938-21-0 |
| Hydrogenated tallow diglycerides | 68553-09-3 |
| Diglyceryl monooleyl ether | 71032-90-1 |
| Diglyceryl tetrastearate | 72347-89-8 |
| Diglycerol caprylate caprate | 72480-00-3 |
| Ethoxylated diglycerol stearate | 72828-11-6 |
| Diglyceryl isostearate | 73296-86-3 |
| Stearoylarachidonylglycerol | 75060-22-9 |
| Panodan SD | 79620-91-0 |
| Diarachidonyl diglyceride | 82231-61-6 |
| Hydrogenated coco mono-, di- and triglycerides | 91744-42-2 |
| 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine monophosphate diglyceride | 130466-13-6 |
| 2',3'-Dideoxycytidine monophosphate diglyceride | 139903-71-2 |
| Tributyrin | 60-01-5 |
| Triolein | 122-32-7 |
| Glyceryl tris(12-hydroxystearate) | 139-44-6 |
| Tripropionin | 139-45-7 |
| Tricaprilin | 538-23-8 |
| Trilaurin | 538-24-9 |
| Tristearin | 555-43-1 |
| Tripalmitin | 555-44-2 |
| Trimyristin | 555-45-3 |
| Tricaproin | 621-70-5 |
| Tricaprin | 621-71-6 |
| Rizolipase | 9001-62-1 |
| Decaglyceryl monooleate | 9007-48-1 |
| Triglycerol stearate | 26855-43-6 |
| Isostearic acid triglyceride | 26942-95-0 |
| Triglyceryl oleate | 33940-98-6 |
| Triglyceryl monostearate | 37349-34-1 |
| Triglyceryl caprylate/caprate | 52622-27-2 |
| Triglycerol | 56090-54-1 |
| Triglyceryl caprylate/caprate | 65381-09-1 |
| Glycerides, tall-oil | 68309-32-0 |
| Triglycerol monolard | 68512-92-5 |
| Triglycerol soya fatty ester | 68605-19-6 |
| Bisulfited blown tall oil fatty acid, triglycerides | 68990-56-7 |
| Triglycerol tricaprylate, caprate | 69070-60-6 |
| Triglycerol pentapelargonate | 72347-87-6 |
| Triglycerol pentalaurate | 72347-88-7 |
| Triglycerol soya fatty ester | 84539-92-4 |
| C10-18 Triglycerides | 85665-33-4 |
| Triglycerol isooctadecanoic acid, mono-, di- and triesters | 90431-25-7 |
| C18-36 Acid triglyceride | 91052-08-3 |
| Hydrogenated coco monoglycerides, diglycerides and triglycerides | 91744-42-2 |
| Trinitrophenylaminolauryl triglyceride | 96337-55-2 |
| 1-(10-Pyrenedecanoyl)-2,3-dioleoylglycerol | 97850-84-5 |
| C8-12 triglycerides | 123465-33-8 |
| Polyglyceryl-3 cetyl ether | 128895-87-4 |
| Triglycerol penta(caprylate-caprate) | 147923-42-0 |
| Tetraglycerol | 56491-53-3 |
| Tetraglycerol octadecanoic acid monoester | 68004-11-5 |
| Tetraglycerol 9-octadecenoic acid monoester | 71012-10-7 |
| Tetraglyceryl monoisostearate | 91824-88-3 |
| 1,1,1-Tris(hydroxymethyl)ethane | 77-85-0 |
| Metriol trinitrate | 3032-55-1 |
| Pentaglycerol | 51555-31-8 |
| Trimethylolpropane | 77-99-6 |
| Decaglyceryl monooleate | 9007-48-1 |
| Hexaglyceryl distearate | 34424-97-0 |
| Hexaglycerol | 36675-34-0 |
| Hexaglyceryl tristearate | 71185-87-0 |
| Hexaglyceryl dioleate | 76009-37-5 |
| Hexaglycerol tetrastearate | 94248-65-4 |
| Hexaglyceryl isostearate | 126928-07-2 |
|
Heptaglycerol |
74899-87-9 |
| Decaglyceryl monooleate | 9007-48-1 |
| Decaglycerol | 9041-07-0 |
| Decaglycerol decaoleate | 11094-60-3 |
| Decaglyceryl dioleate | 33940-99-7 |
| Decaglyceryl tetraoleate | 34424-98-1 |
| Decaglyceryl decastearate | 39529-26-5 |
| Decaglycerol hexaoleic acid hexaester | 65573-03-7 |
| Decaglyceryl decalinoleate | 68900-96-9 |
| Decaglycerol monocaprylic acid, monocapric acid monoesters | 68937-16-6 |
| Decaglycerol decanoic acid and octanoic acid hexaesters | 72479-98-2 |
| Decaglycerol monooleate | 79665-93-3 |
| Decaglycerol docosanoic acid decaester | 84455-45-8 |
| Decaglycerol fatty acids C16-22 decaesters | 84539-89-9 |
| Decaglyceryl pentastearate | 95461-64-6 |
| 1,2,3-Propanetriol, homopolymer, octadecanoate | 9009-32-9 |
| Polyglycerylmethacrylate | 28474-30-8 |
| Polyglycerylmethacrylate | 37310-95-5 |
| Polyglyceryl phthalate ester of coconut oil fatty acid | 66070-87-9 |
| Polyglycerol | 25618-55-7 |
APPEARANCE
2ppm max