PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
TOXICITY
H.S. CODE
CLASSIFICATION
Anti-Infective agent, Antiviral, Enzyme inhibitor, Influenza Treatment, Guanidine, Neuraminidase inhibitor, Dihydropyran, Acetamide
EXTRA NOTES
Used in Influenza treatment.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white to off-white crystalline powder
245 - 255 C
Slightly soluble in methanol, insoluble in ethylether
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Zanamivir
http://www.influenzareport.com/
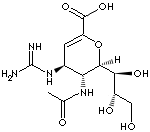
Zanamivir
is an orally inhaled powder currently approved in 19 countries for
the treatment of, and in two for the prophylaxis of influenza A
and B. Zanamivir is a competitive inhibitor of the neuraminidase
glycoprotein, which is essential in the infective cycle of influenza
viruses. It closely mimics sialic acid, the natural substrate of
the neuraminidase (Varghese 1992, Varghese 1995). Zanamivir is administered
via inhalation, resulting in direct delivery to the respiratory
tract, where the concentration has been calculated to be more than
1,000 times as high as the IC50 for neuraminidase. The inhibitory
effect starts within 10 seconds. When systemic involvement of influenza
infection is suspected - as has recently been suggested by some
reports on avian H5N1 influenza in humans (de Jong 2005) - zanamivir
might not be the suitable drug. Over the last few years, a number
of events have resulted in changes to the zanamivir prescribing
information which now contains warnings of bronchospasm, dyspnoea,
rash, urticaria and allergic type reactions, including facial and
oropharyngeal oedema. However, apart from these rare episodes, the
drug has a good safety profile if begun early (Hayden 1997). Co-administration
of orally inhaled zanamivir with inactivated trivalent influenza
vaccine does not seem to adversely affect the production of antihaemagglutinin
antibodies (Webster 1999); a protective antibody response develops
within 12 days (Cox 2001).
http://www.nejm.org/
The
neuraminidase inhibitors zanamivir and oseltamivir interfere with
the release of progeny influenza virus from infected host cells,
a process that prevents infection of new host cells and thereby
halts the spread of infection in the respiratory tract (Figure 1).
Mechanism of Action of Neuraminidase Inhibitors.). Since replication
of influenza virus in the respiratory tract reaches its peak between
24 and 72 hours after the onset of the illness, drugs such as the
neuraminidase inhibitors that act at the stage of viral replication
must be administered as early as possible. In contrast to the adamantanes,
the neuraminidase inhibitors are associated with very little toxicity
and are far less likely to promote the development of drug-resistant
influenza. As a class, the neuraminidase inhibitors are effective
against all neuraminidase subtypes and, therefore, against all strains
of influenza, a key point in epidemic and pandemic preparedness
and an important advantage over the adamantanes, which are effective
only against sensitive strains of influenza A. These new drugs,
if used properly, have great potential for diminishing the effects
of influenza infection.
http://archinte.ama-assn.org/
Zanamivir
for the Treatment of Influenza A and B Infection in High-Risk Patients
APPEARANCE
white to off-white crystalline powder
ASSAY
98.0 ~ 102.0%
SPECIFIC ROTATION
+33° ~ +42°
MELTING POINT
245 ~ 255 C
IMPURITY
Individual impurity: 0.5% max
Total impurity: 1.5% max
LOSS ON DRYING
6.0% max
RESIDUAL SOLVENT
Isopropanol: 0.05% max, Methanol: 0.03% max