ZONISAMIDE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
68291-97-4
TOXICITY
H.S. CODE
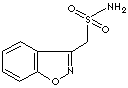
Zonisamide; 3-(Sulfamoylmethyl)-1,2-benzisoxazole;
1,2-Benzisoxazole-3-methanesulfonamide; 3-(sulfamoylmethyl)-1,2-benzisoxazole; Excegran; Zonegran; Zonegran; Zonisamida; Zonisamidum;
c12c(noc1cccc2)CS(N)(=O)=O
CLASSIFICATION
Anticonvulsant, Antioxidant, antiepileptic
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
very slightly soluble
Sparingly soluble in chloroform, n-hexane. Soluble in methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate, and acetic acid.
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
Health hazard: 1, Flammability: 0, Physical hazards: 0
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Zonisamide
PubChem Compound Summary - Zonisamide
Drug Bank - Zonisamide
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Zonisamide
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Zonisamide
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Zonisamide
http://professionals.epilepsy.com/Mechanisms of action of zonisamide: Zonisamide is chemically classified as a sulfonamide. It is not chemically related to any other seizure medicines. The primary mechanisms of action of zonisamide appear related to blockage of voltage-dependent sodium and T-type (but not L-type) calcium channels. Zonisamide is a less potent carbonic anhydrase inhibitor than acetazolamide and therefore this effect is probably not a major contributor to its mechanism of action. Zonisamide is a broad-spectrum anti-epileptic drug (AED) in animal models.
http://www.ema.europa.eu/
Mechanism of action: The mechanism of action of zonisamide is not known, but inhibition of seizure propagation appears to be related at least in part to its ability to both block voltage sensitive sodium and voltage sensitive, type calcium channels, thus reducing the spread of seizure discharges. This mixture of action is comparable to that of other anticonvulsant drugs, such as phenytoin. The role of GABA in zonisamide induced inhibition of seizures is not clear. There does not seem to be a direct effect of zonisamide on GABA mediated mechanism. Other studies suggest that part of its anticonvulsive effects may be by increasing the inhibitory effects of GABA by either affecting GABA binding to its receptor or increasing GABA release in the hippocampus. The effect of zonisamide on carbonic anhydrase activity does not play a significant role in the anticonvulsant activity of the drug. Zonisamide also appears to increase synaptic concentrations of monoamines.
N03AX:
|
Product |
CAS RN. |
|
Sultiame |
61-56-3 |
Phenacemide |
63-98-9 |
Lamotrigine |
84057-84-1 |
Felbamate |
25451-15-4 |
Topiramate |
97240-79-4 |
Gabapentin |
60142-96-3 |
Pheneturide |
90-49-3 |
Levetiracetam |
102767-28-2 |
Zonisamide |
68291-97-4 |
Pregabalin |
148553-50-8 |
Stiripentol |
49763-96-4 |
Lacosamide |
175481-36-4 |
Carisbamate |
194085-75-1 |
Retigabine |
150812-12-7 |
Perampanel |
380917-97-5 |
Beclamide |
501-68-8 |
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.0% min
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.1% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Harmful by ingestion.
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302
P STATEMENTS
![]()
RISK PHRASES
SAFETY PHRASES
22