| CAS
NO. |
107-13-1 |
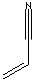
|
| EINECS
NO. |
203-466-5 |
| FORMULA |
H2C=CHCN |
| MOL
WT. |
53.06 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2926.10 |
| TOXICITY |
Oral
rat LD50: 78 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
Acrylon;
Carbacryl; Cyanoethylene; Vinyl Cyanide; |
| Fumigrain;
Propenenitrile; VCN; Acrylnitril; Acrylonitrile monomer;
Akrylonitryl; Cianuro di vinile; Cyanure de vinyle;
Nitrile acrilico; Nitrile acrylique; Akrylonitril; Vinylkyanid;
Cyanoethene; |
| DERIVATION |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
|
| Over
90 percent of world ACRYLONITRILE capacity is based
on the Sohio process for ammoxidation of chemical-grade
propylene. BP brought a new reactor train on line at
Green Lake in late 1996, raising capacity at the site
by 33 percent. In June the company started of
a demonstration unit for its new process for producing
acrylonitrile directly from propane. Acrylonitrile
is usually used for producing Acrylic Fibers,
ABS/SAN Synthetic resin. Acrylamide, synthetic rubber
and Latex. Acrylonitrile is the colorless, odorless
and poisonous liquid, and combines Propylene with ammonia.
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
clear
liquid |
|
MELTING
POINT |
-83
~ -84 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
77
- 78 C |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
0.80
- 0.81 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble |
| pH |
6.0
- 7.5 (5% Aq. Sol.) |
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
1.8 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
480
C
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health:
4; Flammability: 3; Reactivity: 2 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
-1
C |
| STABILITY |
May
undergo autopolymerization with heating, light, bases
and peroxidesmetals or acids. MEHQ is added as
an Inhibitor. Presence of oxygen is necessary for
the inhibitor to function effectively. Should be
stored under an atmosphere containing oxygen 5-21%
by volume. |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
| Adiponitrile,
ABS/SAN resins acrylic fibers, acrylamide, nitrile elastomers,
polymers, polyols, barrier resins and carbon fibers. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
Clear
liquid Free from suspended matter |
| ACETONITRILE |
200ppm
max
|
| ACIDITY |
20ppm
max
|
| ALDEHYDE |
50ppm
max
|
| NONVOLATILES |
100ppm
max
|
| COLOR,
APHA |
10
max
|
| DISTILLATION
RANGE |
74.5
- 79.0 C |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
0.799
- 0.802 |
| INHIBITOR
(MEHG) |
35
- 45 ppm |
| PRECAUTION
IN HANDLING |
Physical
Dangers:The vapour is heavier than air and may travel
along the ground; distant ignition possible.
Chemical
Dangers:The substance polymerizes due to heating, under
the influence of light, bases and peroxides
Heating
may cause violent combustion or explosion. The substance
decomposes on heating producing toxic fumes including
nitrogen oxides, hydrogen cyanide.Reacts violently
with strong oxidants and strong bases causing fire and
explosion hazard.
Routes Of Exposure: The substance
can be absorbed into the body by inhalation of
its vapour, through the skin and by ingestion.
Inhalation
Risk:A harmful contamination of the air can be reached
very quickly on evaporation of this substance
at 20C
Effects Of Short-term Exposure:The substance
and the vapour irritates the eyes, the skin and
the respiratory tract. The substance may cause effects
on the liver and the central nervous system. Exposure
far above the OEL may result in death. The effects
may be delayed.
Medical observation is indicated.
Effects of long-term or repeated exposure: Repeated
or prolonged contact with skin may cause dermatitis.The
substance may have effects on the central nervous
system and liver. This substance is probably carcinogenic
to humans |
|
TRANSPORTATION
|
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
3 |
| UN
NO. |
1093
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| European
Hazard Symbols: T F, Risk Phrases: 11-23/24/25, 38-45,
Safety Phrases: 53-16-45 |
| Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing
trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general
formula RC��N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic
acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound)
excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where
the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O.
Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid.
The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the
presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and
organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl
derivatives from the isomer, HN+��C-.
Sodium cyanide, NaCN; potassium
cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or prussic) acid, HCN
are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides resemble chlorides in
many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including;
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids,
oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons
· Solvent for spinning and casting and
extractive distillation based on its selective miscibility with organic
compounds.
· Removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic
alcohols
· Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic
salts
· Recrystallization of steroids
·
Parent compound for organic
synthesis
· Solvent or chemical intermediate in biochemistry ( pesticide
sequencing and DNA synthesis)
·
High-pressure liquid chromatographic
analysis
· Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex
catalysts
· Stabilizer for chlorinated
solvents
· Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and
pharmaceuticals
|
![]()