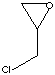| CAS
NO. |
106-89-8 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
203-439-8 |
| FORMULA |
C3H5ClO |
| MOL
WT. |
92.52 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
3-Chloropropyl epoxide; alpha-Epichlorohydrin; Allyl chloride oxide;
|
| 1-Chloro-2,3-epoxypropane;
1-Cloro-2,3-epoxipropano; 1-Chloro-2,3-époxypropane;
1,2-Epoxy-3-chloropropane;
2,3-Epoxypropyl chloride; 2-(Chloromethyl) oxirane; 3-Chloro-1,2-epoxypropane;
3-Chloro-1,2-propylene oxide; 3-Chloropropene-1,2-oxide; 3-Chloropropylene
Oxide;
(Chloromethyl) Ethylene Oxide; (Chloromethyl)oxirane;
DL-alpha-epichlorohydrin; ECH; Epoxy-3-chloropropane; Epoxypropyl chloride; Glycerol Epichlorohydrin; Glycidyl
chloride; (RS)-3-Chloro-1,2-epoxypropane; gamma-Chloropropylene oxide;
|
| DERIVATION |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
Clear liquid
with
an irritating chloroform-like odor |
| MELTING
POINT |
-48
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
116
C |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
1.183 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Moderate
6.59 g/100ml |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
3.3 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
415
C
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 3; Flammability: 3; Reactivity: 2 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
40.5
C |
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
Epichlorohydrin is a clear liquid with a pungent, garlic-like odor. This
substance is highly reactive and flammable compound. It will polymerize under
heating or under strong acid and base conditioms and when contacted with halide
salts. This compound will react violently with strong oxidants, anhydrous metal
halides, strong acids and bases, alcohols, phenols, amines (especially aniline)
and metals such as zinc and aluminium. Fire will liberate explosive and hazard
mixtures including phosgene, hydrogen chloride, and carbon monoxide. It is
strongly irritant to the skin and is carcinogenic. The term of epoxide indicate
three membered cyclic ether (also called oxirane or alkylene oxide) in which
an oxygen atom is joined to each of two carbon atoms that are already bonded to
each other. The unhindered oxygen atom carries two unshared pairs of electrons -
a structure which favors the formation of coordination complexes and the
solvation of cations. Because of equilateral triangle strain in this small ring,
epoxides are more reactive than larger ring ethers. Epoxides undergo reactions
such as C–O bond cleavage, nucleophilic addition, hydrolysis and reduction under
mild conditions and more rapidly than other ethers. Epoxides are formed by some
oxidation reactions of alkenes with peracids. Epichlorohydrin, called also
chloropropylene oxide, is prepared from propene, which is chlorinated to allyl
chloride. The allyl chloride is the feed to yield glycerol chlorohydrins, which
produce epichlorohydrin under dehydrochlorination with alkali. Epichlorohydrin
is used to make numerous substances, predominantly synthetic glycerin and
unmodified epoxy resins. It is used as a building block in making elastomers and
other polymers, some of which are used in water supply systems. It is used in
making wet strength resins and water-treatment resins. It is used to make a
variety of glycidyl derivatives, surfactants, plasticizers, dyestuffs,
pharmaceuticals, emulsifiers, lubricants, and adhesives. It is used as an insect
fumigant. It is also used as a solvent for cellulose, resins, rosins, paints ,
and pesticide, and as a stabilizer in chlorine-containing substances. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
Clear liquid
with
an irritating chloroform-like odor |
|
PURITY |
99.9%
min |
|
COLOR,
APHA
|
15
max
|
|
SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
1.18
- 1.185
|
|
BOILING
POINT |
115
- 117 C |
|
VISCOSITY
cps |
1.12
at 20 C
|
|
MOISTURE |
500ppm
max |
|
TRANSPORTATION
|
| PACKING |
230kgs
in drum |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
6.1
(Packing Group: II) |
| UN
NO. |
2023
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard Symbols: T, Risk Phrases: 45-10-23/24/25-34-43, Safety
Phrases: 53-45 |