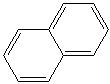
NAPHTHALENE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
91-20-3
H.S. CODE
CLASSIFICATION
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white solid
Insoluble (3mg/100ml)
AUTOIGNITION
567 C
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Naphthalene
PubChem Compound Summary - Naphthalene
IPCS INCHEM - Naphthalene
http://www.hpa.org.uk/
Naphthalene
is the most abundant component of coal tar, the liquid residue formed
during the distillation of coal into coke. Coke is distilled from
coal to remove many of the impurities, leaving a carbonaceous solid
which produces little or no smoke when burnt, and as such is used
as a smokeless fuel. Distillation of the coal tar itself, can yield
around 50% naphthalene, which following treatment with sodium hydroxide
and sulphuric acid to remove impurities can be fractionally distilled
to yield approximately 95% pure naphthalene. Naphthalene is released
into the environment upon burning organic materials, such as fossil
fuels and wood. As such, naphthalene is a constituent of industrial
and vehicle exhaust emissions due to its presence in coal and petroleum.
Naphthalene is also released when tobacco is burnt and is therefore
also found in cigarette smoke. The most common current use for naphthalene
is as a raw material in the production of phthalic anhydride, which
is used in the manufacture of dyes, plasticizers and insecticides.
It is also used in the production of some pharmaceutical preparations.
Naphthalene can be used as a fumigant for repelling moths and therefore,
was historically used in mothballs. Its use in mothballs has since
been limited due to both the flammability and toxicity of naphthalene.
Naphthalene is a component of coal tar creosote, which was used
as a wood preservative, however, in the European Union its use has
since been banned for amateur and unlicensed professional applications
due to the health effects of not only naphthalene but also the many
other toxic constituent compounds.
http://www.beyondpesticides.org/
Naphthalene
is currently used in the manufacture of phthalic anhydride, which
is used as an intermediate in the production of phthalate plasticizers,
resins, dyes, pharmaceuticals, insect repellents, and other materials.
Naphthalene is also a component of crude oil and also occurs naturally
in the essential oils of the roots of Radix and Herba ononidis.
Studies involving rabbits and pregnant rats have reported treatment
related signs of neurotoxicity; lethargy, slow respiration including
periods of apnea, and/or inability to move a�er dosing. Subchronic
studies however, have found no clinical signs of neurotoxicity.
Naphthalene has been shown to be a weak developmental and reproductive
toxicant with detectable effects occurring only at doses associated
with substantial maternal toxicity.
Local:
Naphthalene is a white, volatile aromatic hydrocarbon with characteristic odor;
insoluble in water, somewhat soluble in methanol/ethanol, soluble in organic
solvents and very soluble in ether, chloroform, or carbon disulfide.
Commercially it is available in molten form or in flaked form. It has the
molecular structure of two fused or condensed benzene rings sharing two adjacent
carbon atoms; C10H8. Naphthalene is obtained from coal tar which is distilled in
the temperature range of 170 - 230 C and is treated with a sodium hydroxide
solution to remove phenols. Naphthalene is obtained by the isolation from pyrolysis residue oils, olefin
fractions, and petroleum-derived fractions. The distribution capacity is supposed
to be about 60% coal-tar and 40% petroleum-derived naphthalene
in U.S.A. It is an important parent material to produce
numerous substitution products used in the manufacture of dyes, insecticides,
organic solvents and synthetic resins. Phthalic anhydride is prepared by
oxidizing naphthalene to be used in the manufacture of dyes, resins,
plasticizers, and insecticides. Naphthalene sulfonate surfactants and
dispersants, however, have increased their market share significantly and are
expected to drive whatever growth there is for naphthalene. Naphthalene is the
major raw material for Carbaryl, used as a general-purpose insecticide.
Naphthalene is also used for moth repellents, fungicides, lubricants,
explosives, wood preservatives, vermicides and hydronaphthalenes (tetralin,
decalin). Hydronaphthalenes are used for major raw material
for dyes, resins, plasticizers, and insecticides. They are also used in reactive
and process solvents, heat transfer fluid, dye carrier, fuel additives,
lubricants, ore flotation and oilfield chemicals.
|
APPEARANCE
brown flake
PURITY
95.0 % min (JIS K 2436)
NON-VOLATILES
0.3 % max (JIS K 2436)
ASH
0.1% max (JIS K 2436)
FREEZING POINT
77.5 min (JIS K 2436)
SULFUR CONTENT
0.7 % max (ASTM D 129-91)
TRANSPORTATION
1334
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Flammable solid. Harmful if swallowed. Possible cancer hazard. May cause cancer based on animal data. May cause skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritation. Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. OSHA Hazards: Flammable solid, Carcinogen, Highly toxic by inhalation, Toxic by ingestion, Irritant. Target Organs: Eyes, Blood, Kidney, Lungs, Central nervous system, Liver, Heart
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS



HAZARD STATEMENTS
H228
Flammable solid.
H302 Harmful if swallowed.
H315 + H320 Causes
skin and eye irritation.
H330 Fatal if inhaled.
H351 Suspected
of causing cancer.
H400 Very toxic to aquatic life.
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P210
Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. - No smoking.
P260
Do not breathe dust/ fume/ gas/ mist/ vapours/ spray.
P273 Avoid
release to the environment.
P281 Use personal protective equipment
as required.
P284 Wear respiratory protection.
P305 + P351
+ P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes.
Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
P310
Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/ physician.
![]() Xn
Harmful
Xn
Harmful![]() N
Dangerous for the environment
N
Dangerous for the environment
RISK PHRASES
22
Harmful if swallowed.
40 Limited evidence of a carcinogenic
effect.
50/53 Very toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause
long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.
SAFETY PHRASES
36/37
Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves.
46 If
swallowed, seek medical advice immediately and show this container
or label.
60 This material and its container must be disposed
of as hazardous waste.
61 Avoid release to the environment.
Refer to special instructions / safety data sheets.
PRICE INFORMATION