PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
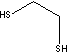
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
clear liquid
-41 C
1.123
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
clear to yellowish liquid
99.0% min
0.5% max
|
|
|
| 1,2-ETHANEDITHIOL | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 540-63-6 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 208-752-3 | |
| FORMULA | C2H4(SH)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 94.20 | |
| H.S. CODE |
|
|
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | 1,2-Dimercaptoethane; 1,2-Dithiol ethane; Dithioethyleneglycol; | |
| Dithioglycol; Ethyl hydropersulfide; Ethylene dimercaptan; Ethylene dithioglycol; Ethylenedimercaptan; Ethylenedithiol; S-Ethylene dimercaptan; s-Ethylene dimercaptan; | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
clear liquid |
|
| MELTING POINT |
-41 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 146 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.123 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | slightly soluble (soluble in most organic solvents) | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| AUTOIGNITION | ||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 94 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Acetals are geminal-diether derivatives of aldehyde by combination of an aldehyde molecule with two alcohol molecules and elimination of water. Thioacetal is the sulfur analogs of acetal. Thiols give thioacetals with Lewis acid catalyst. Ethanedithiol reacts with aldehydes to give dithiolanes. Oxidation alcohols to aldehydes changes the oxidation state of carbon but not oxygen. Oxidation of sulfur compounds changes the oxidation state of sulfur rather than carbon, which inverts the polarity at the functionalised carbon atom. This polarity inversion allows next step reactions of this functional group and new transformations. Ethanedithiol is the starting material of dithiane chemistry. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to yellowish liquid |
|
| ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|
| WATER |
0.5% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 3071 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: T, Risk Phrases: 10-21/22-23-36, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37-45 | ||
|
|
|