PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
|
Product |
CAS RN |
|
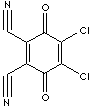
2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone |
84-58-2 |
| o-Chloranil |
2435-53-2 |
| Phenylbis(trifluoroacetato-O)iodine |
2712-78-9 |
|
p-Chloranil |
118-75-2 |
|
Tritylium tetrafluoroborate |
341-02-6 |
|
Selenium dioxide |
7446-08-4 |
|
Manganese dioxide |
1313-13-9 |
APPEARANCE
MELTING POINT
214 C min
ASH
0.1% max