PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
MOISTURE
|
|
|
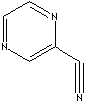
| 2-CYANOPYRAZINE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 19847-12-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 243-369-5 | |
| FORMULA | C5H3N3 | |
| MOL WT. | 105.10 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Pyrazine-2-carbonitrile; Pirazinacarbonitrilo; | |
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear to pale yellow liquid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
20 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 198 - 200 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.173 - 1.174 | |
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble (10mg/ml) | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |
| AUTOIGNITION | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| NFPA RATINGS | 1.534 | |
| FLASH POINT | 103 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Pyrazine, hygroscopic white solid, is an aromatic nitrogen compound characterized by a ring structure contains 4 carbon atoms with two nitrogen atoms at 1 and 4 positions (paradiazine); melting at 55 - 56 C, boiling at 115 - 116 C. Pyrazine is freely soluble in water. It is fused to form many polycyclic compounds, as useful structures in pharmaceuticals and perfumes. It is a component of the folates (vitamin B compounds) and of the isoalloxazine ring nucleus of flavins. Numerous pyrazine derivatives such as pyrazine polycyclic compounds, alkyl-, alicyclic-, and alkylaryl-substituted compounds, derivatives containing oxygenated functional groups and thio- functional groups in the side-chains are used in biological, drug, flavouring and perfumery industry. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to pale yellow liquid | |
| ASSAY (G.C) | 99.0% min | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.1% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/21/22-36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-36 | ||
|
|
||
| Nitrile is any of a family of organic compounds containing cyano group (-C≡N) which is attached to a carbon atom and having the general formula RC≡N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic acid' to '-onitrile', or '-nitrile', whichever preserves a single letter o. Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid. Pendant nitriles are often named as “cyano” substituents. | ||
|
|
|