PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
90.0% min
WATER
6.0% max
|
|
|
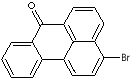
| 3-BROMOBENZANTHRONE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 81-96-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 201-390-7 | |
| FORMULA | C17H9BrO | |
| MOL WT. | 309.16 | |
| H.S. CODE |
| |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | 3-Bromo-7H-benz(de)anthracen-7-one; 3-Bromobenz(d,e)anthrone; | |
| 7-Bromomesobenzanthrone; 7-Bromomesobenzanthrone; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | brown to green powder | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | insoluble | |
| AUTOIGNITION | ||
| NFPA RATING | Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Benzanthrone is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, with melting point 170 C; insoluble in water. Traditionally it is used as a compound for dyes and other coloring agents. Benzanthrone is a basic substance with fluorescent and luminescent properties. Its applications find in photosensitizing and charge transport material. The transportation of charges is responsible for fluorescence and electrical energy. Benzanthrone structure material is an organic semiconductor oligomer which can provide some merits of self radiation, flexibility, light weight, easy fabrication, and low cost in photovoltaic and display devices. Substituted benzanthrones are used in the preparation of fluorescent dyes. Violanthrone is the material with the structure of dibenzanthrone-fused. Other examples include pyranthrone, flavanthrone, anthanthrone and isoviolanthrone. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
brown to green powder | |
| PURITY |
90.0% min | |
|
WATER |
6.0% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| REMARKS | ||
| Hazard Symbols: n/a, Risk Phrases: n/a, Safety Phrases: 24/25/28A/37/45 | ||
|
|
|