PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
CONTENT
99.0% min (HPLC)
MELTING POINT
|
|
|
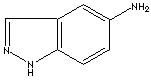
| 6-AMINOINDAZOLE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 6967-12-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 230-177-1 | |
| FORMULA | C7H7N3 | |
| MOL WT. | 133.15 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
|
|
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Indazol-6-yl Amin; Indazol-6-il Amina; Indazole-6-yl Amine; | |
| Indazol-6-yl Amine; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to yellow powder | |
|
MELTING POINT |
204 - 206 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
||
| pH |
| |
| VISCOSITY |
| |
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Indazole is another name of benzopyrazole which has the pyrazole ring (five-membered unsaturated ring structure composed of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms at 1,2 positions) fused to benzene ring. Indole is the compound that pyrrole (haing one nitrogen atom) is fused to benzene ring. There are tautomerer of indole. They are called indolenine (unsubstituted 3H-indole) The structural isome of indole is called isoindole. Indoline is dihydroindole. Benzimidazole is the compound that imidazole ring (containing two nitrogen atoms at nonadjacent positions) is fused to benzene. These structure compounds are important in agrochemical industry. They are fundamental structures of fungicides, herbicides, and plant growth regulators. These compounds are used in the production of amino acids, perfumes, colorants, and medicines. Indazole class compounds can be applied in the field that photodynamic activity is needed. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to yellow powder | |
|
CONTENT |
99.0% min (HPLC) | |
|
MELTING POINT |
204 - 206 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22-36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-37/39 | ||
|
|
|