PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
30866-95-6 (hydrochloride salt)
60908-54-5 (dihydrochloride salt)
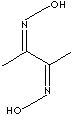
CH3C(=NOH)C(=NOH)CH3
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
OXIMES /
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
Oxime is any compound with the general formula R\R'/C=N-OH, where R and R' are hydrogen atoms or organic groups. Oximes are condensation products of hydroxylamines with aldehydes (forming aldoxime), ketones (forming ketoxime), or quonone. Aldoximes exist only as a syn isomer. But benzaldoxime (aromatic aldoximes) exist in syn- and anti isomers: the syn form melts at 34C, antiisomeric form at 130 C; both forms are soluble in ethanol and ether.
There are two geometrical isomer: syn and anti isomer (the term syn-anti isomerism is for stereoisomers by other atoms' unsaturated bond rather than carbon). Two isomers have very different properties. The conversion of oximes into corresponding amides, known as Beckmann rearrangement (usually using sulphuric acid as a catalyst), is used to make synthetic fiber monomers. Cyclhexanone oxime is converted into its isomer epsilon-caprolactam which is the raw material to make nylon-6. The amides obtained by Beckmann rearrangement can be converted into amines by hydrolysis, which are useful in the manufacture of dyes, plastics, synthetic fibres, and pharmaceuticals.Oximes are used as a peel-preventing additive in paints and lacquers. It acts as an antioxidant against oxidative drying materials which forms sticky skin with air oxygen. The another effect of anti-skinning offers drying time delay which can be used in formulating paints.
Oximes are used as chemical building block for the synthesis of agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. In medicine application, Oxime structure is effective in cholinesterase reactivators to treat the poisoning by organophosphates. Example of these drugs are pralidoxime, obidoximine, methoxime, asoxime, and trimedoxime. Oxime moiety is found in some cephalosporin antibiotics. Diacetyl monoxime is used as an inhibitor of ATP-sensitive potassium ion channels.
Diacetyl (dimethylglyoxal) reacts with hydroxylamine to produce diacetyldioxime (dimethylglyoxime). The characteristic property of oxime is the scavenging free radical and oxygen. Diacetyl oxime is used as a chelating agent. An application example is the spectrophotometric determination of Co(II), Fe(II), Ni(II), Pd(II) and Re(VII)1. Dimethylglyoxime reacts with a nickel salt in a green solution to generate a red colored insoluble tetradentate coordinate complex of nickel. It is used as a reagent for the colorimetric determination of urea and ureido compounds.
Oxime is used as a ligand in transition-metal complex catalyst chemistry. Oxime acts as an antioxidant, radical scavenger which find applications in textile, plastic, paint, detergent, and rubber industry.
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
WATER
0.05% max
ASH
0.1% amx
INSOLUBLES
0.05% max (in Alcohol)
MELTING POINT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF HYDROXYLAMINE
Hydroxylamine is a white crystalline compound containing nitrogen with the formula of NH2OH and is therefore an ammonia (NH3) like compound. In the nature, hydroxylamine is an biological intermediate in the nitrification (biological oxidation of ammonia with oxygen into nitrite ) and in the anammox (biological oxidation of nitrite and ammonium into dinitrogen gas) which are important in the nitrogen cycle in soil and in wastewater treatment. Hydroxylamine is obtained commercially by acid hydrolysis of nitroparaffins or by the modified reduction of nitric acid. It is used as a powerful reducing agent in photography and in organic synthesis. It converts aldehydes (and ketones) to oximes (caprolactam), and acid chlorides to hydroxamic acids. It is used as a catalyst or inhibitor in polymerization processes. It is used in enzyme reactivation. It is used as an antioxidant in fatty acids and soaps. The nitrate form of hydroxylammonium is used as a rocket fuel which is burned with an oxidizer to produce thrust. Hydroxylamine tends to be explosive when heated. Its derivatives in the form of salts are more stable to be used and handled. Hydroxylamine Hydrochloride is used as an auxiliary in photographic industry to prevent discolouration. It is a polymerization inhibitor or free radical scavenger against solid bond monomers such as olefin, styrene, butadiene, isoprene and divinylbenzene. It is also used in rubber synthesis processes as a non-discoloring short stoppers. Diethylhydroxylamine has the property of oxygen scavenging and used in water treatment chemical formulation to prevent corrosion. It is used as an auxiliary in photographic industry to prevent discolouration. It is a vapour phase polymerization inhibitor against solid bond monomers such as olefin, styrene, butadiene, isoprene and divinylbenzene. It is used as a stabilizer for phenolics. It is used as an intermediate for pharmaceuticals and water treatment chemicals. It is also used as a raw material of silicon sealant and coating materials. Hydroxylammonium salts find applications in the field of :
- Organic synthesis: preparation of oximes, hydroxamic acids from carboxylic acids, N- and O- substituted hydroxyamines, and addition reactions of carbon-carbon solid bond.
- Surface treatments: preparation of anti-skinning agents, corrosion inhibitors, metal cleaner additive
- Starting material for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals manufacturing
- Rubber and plastic industry: antioxidant, vulcanization accelerator, radical scavenger.
- Textile industry: fixative for textile dyes, auxiliary in some dyeing processes. bleaching
- Metallurgy: Metal extraction and flotation aid
- Aantioxidant in fatty acids and soaps
- Photographic auxiliary as a stabilizer of colour and emulsion additive for colour films.