PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
yellow to reddish liquid
0.942
146 C
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
yellow to reddish liquid
95.0% min
MELTING POINT
|
|
|
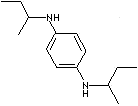
| N,N'-DI-SEC-BUTYL-P-PHENYLENEDIAMINE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 101-96-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-992-2 | |
| FORMULA | C14H24N2 | |
| MOL WT. | 220.36 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | N,N'-Bis(1-methylpropyl)-1,4-phenylenediamine; Tenamene 2; | |
| N,N'-Di-sec-butil-p-fenilendiamina; N,N'-di-sec-butyl-p-phénylenediamine; N,N'-Bis(1-methylpropyl)-1,4-benzenediamine; Du Pont Gasoline Antioxidant No. 22; | ||
| DERIVATIVE |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
yellow to reddish liquid |
|
| MELTING POINT | 15 - 18 CC | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.942 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | < 0.1 g/100ml at 20 C | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
| FLASH POINT |
146 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| There are three isomers of phenylenediamine: ortho-, meta-, and para-phenylenediamine. They are low toxic diamines used as components of plastic composites and engineering polymers. Phenylenediamine moiety compounds are used to produce aramid fibers, dyes including hair dyes, rubber chemicals (vulcanization accelerators and antioxidants), and pigments. Antioxidant is a substance added in small quantities to hydrocarbons which are susceptible to oxidation, such as rubbers, plastics, foods, and oils to inhibit or slow oxidative processes, while being itself oxidized. Antioxidants work in two different ways. In primary antioxidants (also called free-radical scavengers), antioxidative activity is implemented by the donation of an electron or hydrogen atom to a radical derivative. These antioxidants are usually hindered amines (p-Phenylene diamine, trimethyl dihydroquinolines, alkylated diphenyl amines) or substituted phenolic compounds with one or more bulky functional groups such as a tertiary butyl at 2,6 position commonly. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is a common example of hindered phenolic antioxidant. The reaction rate, or carbocation stability, in SN1 mechanism is 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3 (no SN1) so, tertiary alkyl moiety exists in lots of phenolic antioxidant compounds. Primary antioxidants are free radical scavengers which combine with peroxy radicals and break autocatalytic cycle. In secondary antioxidants ( also called peroxide decomposers), activity is implemented by the removal of an oxidative catalyst and the consequent prevention of the initiation of oxidation. Examples of peroxide decomposer type of antioxidant are trivalent phosphorous and divalent sulfurcontaining compound such as sulfides, thiodipropionates and organophosphites. Synergistic effect is expected when primary antioxidants are used together with secondary antioxidants as primary antioxidants are not very effective against the degradation by UV oxidation. Sometimes, chelating agents are added to scavenge metal impurities which can initiate decomposition. N,N'-di-sec-butyl-p-phenylenediamine is used as an antioxidant for fuel, lube oil, and lipids (mineral oils and plant oils). | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow to reddish liquid |
|
| CONTENT |
95.0% min |
|
|
MELTING POINT |
15 - 18 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 185kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 2922 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 25-34-43-50/53, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37/39-45-61 | ||
|
|
|