PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
2902.90.9000
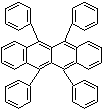
SMILES
c12c(c(c3c(cccc3)c1c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1)c(c1ccccc1)c1c(cccc1) c2c1cc ccc1
CLASSIFICATION
Polycyclic aromatic compound, Fluorescent dye
EXTRA NOTES
Chemiluminescent activator.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
dark red crystals
332 - 334 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
USA.gov - Rubrene
Wikipedia Linking - Rubrene
Google Scholar Search - Rubrene
PubChem Compound Summary - Rubrene
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Rubrene
Material Safety Data Sheet - Rubrene
EPA - Substance Registry Services - Rubrene
Local:
Due to extended pi-electron cloud overlaps, organometallic molecules or aromatic oligometers such as anthracene exhibit semiconductor properties. Conductive polymers have extended delocalized bonds that creates electrical conductivity when charge carriers generated make positive charges (holes) and negative charges (electrons) move to opposite electrodes. Doping is the intentional impurities in a pure semiconductor to generate charge carriers. The transportation of charges is responsible for fluorescence and electrical energy. These can form well-ordered thin crystalline films. Organic semiconductors have some merits of self radiation, flexibility, light weight, easy fabrication, and low cost. Organic electroluminescence materials have lead to the rapid development of photovoltaic and display devices such as organic solar cells, biosensitizers, OLED(Organic Light Emiting Diode), OTFT(Organic Thin Film Transistor), Wearable Display, and e-Paper. Some examples of organic electroluminescence materials are:
- Oligomer Electro Luminescence Materials
- 8-hydroxyquinoline aluminum
- Anthracene
- Pentacene
- Penyl substituent cyclopentadiene derivatives
- Phthaloperinone derivatives
- Perylene derivatives
- Rubrene
- Polymer Electro Luminescence Materials
- Polyanilines
- Poly(p-phenylenevinylene)s
- Poly(thiophene)s
- Poly(alkylfluorene)s
- Poly(acetylene)s
Chemoluminescence (or chemiluminescence) is the luminescence (light emission) generated as the result of direct transformation of chemical energy into light energy without showing a corresponding degree of heat. When the reactants are oxidized in the presence of catalysts, they yield intermediate complexes which get rid of the extra energy quickly in the form of light (ultraviolet, visible, or infrared) photons to become a lower energy level products. Luminol (3-Aminophthalhydrazide) is a chemoluminescent dye. It is used for biological detection of metal cations and blood. The iron in haemoglobin acts as a catalyst to accelerate the process. Luciferins are bioluminescence emitting light pigments originated by an organism like bacteria, fungi, fireflies and deep sea fish. Enzymes and proteins associated with bioluminescence have been developed for biomedical research. Coelenterazine, substrate for luciferase and photoprotein, is used as a intracellular luminophore as to measure changes in oxide and Ca2+ levels in aequorin cells. Fluorescence such as fluorescein undergoes light-emission processes, but the energy source is light absorption from an external source.
Some Chemoluminescence related compounds include:
- Bis(2,4,5-trichlorophenyl-6-carbopentoxyphenyl) oxalate (CAS #: 30431-54-0)
- Bis(2,4,6-trichlorophenyl) Oxalate (CAS #: 1165-91-9)
- Bis(2,4-dinitrophenyl) Oxalate (CAS #: 16536-30-4)
- 9,10-Bis(phenylethynyl)anthracene (CAS #: 10075-85-1)
- 9,10-Diphenylanthracene (CAS #: 1499-10-1)
- Rubrene (CAS #: 517-51-1)
- Bis(2-carbopentyloxy-3,5,6-trichlorophenyl)oxalate (CAS #: 75203-51-9)
- N-(4-Aminobutyl)-N-ethylisoluminol (CAS #: 66612-29-1)
- Luminol (CAS #: 521-31-3)
- Isoluminol (CAS #: 3682-14-2)
- 5,12-Bis(phenylethynyl) naphthacene (CAS #: 18826-29-4)
- 2-Chloro-9,10-bis(phenylethynyl) anthracene (CAS #: 41105-36-6)
- 1,8-Dichloro-9,10-bis(phenylethynyl) anthracene (CAS #: 51749-83-8)
- Lucifer Yellow CH dipotassium salt (CAS #: 71206-95-6)
- Lucifer yellow VS dilithium salt (CAS #: 71231-14-6)
- Lophine (CAS #: 484-47-9)
- Tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene (CAS #: 996-70-3)
- Luciferins (Firefly luciferin, Bacterial luciferin, Dinoflagellate luciferin, Vargulin)
- Coelenterazine
- 2-(4-Dehydroxy) coelenterazine
APPEARANCE
dark red crystals
98.0% min
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Not a dangerous substance. Potential Health Effects: Eyes - May cause eye irritation. Skin - May be harmful if absorbed through skin May cause skin irritation. Inhalation - May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. Ingestion - May be harmful if swallowed.
RISK PHRASES
SAFETY PHRASES