PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
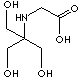
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Buffer is a substance, generally a solution, that can keep its pH constant,
despite the addition of strong acids or strong bases and external influences of
temperature, pressure, volume, redox potential. Buffer prevents change in the
concentration of another chemical substance, e.g., proton donor and acceptor
systems that prevent marked changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH). Many
acid-base reactions take place in living organisms. However, for organisms to
perform certain vital functions, the body fluids associated with these functions
must maintain a constant pH. For example, blood must maintain a pH of close to
7.4 in order to carry oxygen from the lungs to cells; blood is therefore a
powerful buffer. The commonest buffer in chemical solution systems is the
acid-base buffer.
- Bicarbonate buffer; a buffer system composed of bicarbonate ions and dissolved carbon dioxide; in the body, this system is an important factor in determining the pH of the blood as the concentration of bicarbonate ions is regulated by the kidneys and of carbon dioxide by the respiratory system.
- Cacodylate buffer; one containing an organic arsenical salt, used in preparing fixatives for electron microscopy.
- Phosphate buffer, a buffer system composed of KH2PO4 and Na2HPO4; in the body, it is important in regulating the pH of the renal tubular fluids; when 0.025 molal (equimolal of the potassium and sodium salts), the pH is 6.865 at 25 C.
- Protein buffer, a buffer system involving proton donor and proton acceptor groups of the amino acid residues of proteins.
- TRIS buffer (tromethamine): an amine base used intravenously as an alkalizer for the correction of metabolic acidosis. The pH values of all buffers are temperature- and concentration-dependent. For Tris buffers, pH increases about 0.03 unit per C temperature decrease, and decreases 0.03-0.05 unit per ten-fold dilution.
- Veronal buffer; a barbital buffer commonly used in the preparation of fixatives for electron microscopy.
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
INSOLUBLES
0.01% max
LOSS ON DRYING
1.0% max
HEAVY METALS
5ppm max
CLARITY
clear (in 40% water)
pH
Fe
1ppm max