PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
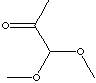
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
clear to yellow liquid
-57 - -56 C
140 - 145 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Acetals are geminal-diether derivatives of aldehyde by combination of an aldehyde molecule with two alcohol molecules and elimination of water. The formula is RCH(OR')2, where R and R' are aliphatic or aromatic radicals. If the formula is RCR'(OR")2, it is called ketal derived by a combination of a ketone with two alcohols. The "acetal" also refer to independent structural units in certain biological and commercial polymers. Lower acetals are colorless volatile liquid used as a solvent and in cosmetics but higher acetals are solid. It is soluble in ether and alcohol but slightly soluble in water. It is unstable in acid but stable in base.
Acetal polymers (polyacetals) are tough and hard plastics used as substitutes for metals. Acetal homopolymers are produced by the polymerization of formaldehyde. Acetal copolymers are produced are by the polymerization of formaldehyde with trioxane. In nature the most stable glucose exists as a cyclic hemiacetal and maltose is an acetal made from two glucose units.
Acetal formation is reversible (hydrolyzed back to their starting components by treatment with aqueous acid). In order to achieve effective acetal formation an acid catalyst must be used and the water produced with the acetal must be removed. p-Toluene sulfonic acid is often used as a catalyst in the formation of acetal which water must be removed from the reaction mixture to escape reversible reaction. Water is removed azeotropically by distilation. (Toluene is the solvent). A way to remove water is to use an orthoester as a source of alcohol; water produced along with the acetal product is used up in hydrolysing the orthoester and producing more alcohol to be used in the reaction. Orthoester is a functional group which has three alkoxy groups attached to one carbon atom.
The importance of acetals as carbonyl derivatives lies chiefly in protecting groups for carbonyl groups in organic synthesis as they exhibit stability and lack of reactivity in neutral to strongly basic environments. Acylals, with the general formula R-C(OOCR)2, is an another carbonyl protecting group. It is obtained by the reaction of aldehydes with acetic anhydride. Acetal molecules are used as an intermediate for the production of polymers, vitamins, carotenoid pigments, dyes, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, corrosion inhibitors, fragrances and perfumes.
APPEARANCE
clear to yellow liquid
98.0% min
0.5% max