PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
130-00-7
204-973-4
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
light yellow powder
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
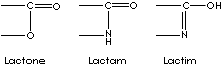
Lactone is an internal cyclic monoester (anhydride) derived from the hydroxyl and carboxyl radicals of gamma or delta hydroxy acids by the removal of a H2O between a carboxyl and a hydroxyl group in the same molecule; gamma-hydroxybutyric acid forms gamma-butyrolactone and delta-hydroxydecanoic acid forms delta-decalactone spontaneously. In result, prefixes describe the ring size: beta- is for 4-membered ring), gamma- , 5-membered, and delta-, 6-membered ring. Lactam (a cyclic amide) is the nitrogen analog of lactone. Gamma-aminobutyric acid forms gamma-butyrolactam (also called 2-pyrrolidinone). Lactim is the tautomeric enol form of lactam. Lactam structure, a heteroatomic cyclic amide compound, is an important part in antibiotics such as penicillin. These structures, cyclic esters and analogues, are active nucleuses in pharmacological activity and flavorings. Their good solvency properties also useful in industrial application. Lactams have big demand in artificial fibre industry. They are polymerizable and used as nylon precursors.
1,8-Naphtholactam is used as an intermediate for dyes, pigments and fluorescent whiteners.
APPEARANCE
light yellow powder
98.0% min
OTHER INFORMATION