PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
947-19-3
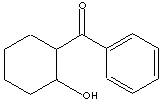
HOC6H10COC6H5
204.27
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Health: 2, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking (Photoinitiator)
Local: Photoinitiators are compounds that break down into free radicals upon exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Photoinitiators undergo a unimolecular bond cleav-age upon irradiation to yield free radicals (Benzoin Esters; Benzil Ketals; alpha-Dialkoxy Acetophenones; alpha-Hydroxy-alkylphenones; alpha-Amino Alkyl- phosphine; Acylphosphine Oxides). Another type of photoinitiators undergo a bimolecular reaction where the excited state of the photoinitiator interacts with a second molecule (a coinitiator) to generate free radicals(Benzo Phenones,amines; Thioxanthones,amines; Titanocenes). Photoinitiators are widely applied in UV curing inks, wood coatings, paper coatings, optical fiber, PCB, screen printing , paper varnish and other surface coatings.
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
99.0% min
0.5% max
0.1% max
TRANSPARENCE
99.0% min ( 500nm), 98.% min ( 425nm)
Skin Contact: May cause skin irritation. Skin Absorption: May be harmful if absorbed through the skin. Eye Contact: Causes eye irritation. Inhalation: May be harmful if inhaled. Material may be irritating to mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. Ingestion: May be harmful if swallowed.