PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
82799-44-8
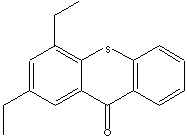
164.20
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
110 C
APPLICATIONS
- Peroxides including hydroperoxides (tertiary-butyl hydroperoxide, benzoylperoxide)
- Azocompound thermal initiators (azoisobutyronitrile)
- Redoxinitiators (mixture of iron(III) acetylacetonate): free radicals are formed by one-electron transferreactions. Useful in low temperature and emulsion polymerization
- Photoinitiators (benzoin, benzil dimethylketal)
The main advantage of polymerization started by photoinitiators is temperature-independence and easy control. It can be conducted at very low temperatures and can be stopped simply by removing the light source. Photoinitiators are compounds that break down into free radicals upon exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Photoinitiators undergo a unimolecular bond cleavage upon irradiation to yield free radicals (benzoin esters; benzil ketals; alpha-dialkoxy acetophenones; alpha-hydroxy-alkylphenones; alpha-amino alkyl- phosphine; acylphosphine oxides). Another type of photoinitiators undergo a bimolecular reaction where the excited state of the photoinitiator interacts with a second molecule (a coinitiator) to generate free radicals(benzo phenones,amines; thioxanthones,amines; titanocenes). Photoinitiators are widely applied in UV curing inks, wood coatings, paper coatings, optical fiber, PCB, screen printing , paper varnish and other surface coatings.
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
97.0% min
66 - 71 C
VOLATILES
0.5% max