PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
58 ~ 60 C
pH
141 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
USA.gov - 2-Methylindole
Wikipedia Linking - 2-Methylindole
Google Scholar Search - 2-Methylindole
U.S. National Library of Medicine - 2-Methylindole
PubChem Compound Summary - 2-Methylindole
NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) - 2-Methylindole
Material Safety Data Sheet - 2-Methylindole
Human Metabolome Database - 2-Methylindole
EPA - Substance Registry Services - 2-Methylindole
Local:
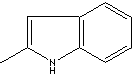
Indole, benzopyrrole, is a yellow crystalline powder with unpleasant aroma. It has the pyrrole ring (five-membered unsaturated ring structure composed of four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom) which is fused to benzene ring. There are tautomerer called indolenine (unsubstituted 3H-indole) and structural isomer, isoindole. But they are unstable. Indole occurs in some plants or in coal tar, and is formed in the intestine during putrefaction and by certain cultures of bacteria. it is commercially synthesized from phenylhydrazine and pyruvic acid. Indole structure is a motif in nature. Prominent examples include tryptophan (aromatic side chain amino acid), serotonin (neurotransmitter), auxin (plant growth hormone), and indigo (plant colorant). One more interesting point is all these compounds have functional branches at 3 position. Indole is used in perfumery and in preparing tryptophan, one of the 20 amino acids commonly found in animal proteins. It has important application in the industry of plant growth. It is used to prepare indoleacetic acid (auxin) and other plant growth substances which help the development of roots in plant. It is used to make selective herbicides. Indole and its derivatives are widely used in making perfumes, dyes, agrochemicals and medicines. 2-Methylindole is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of dyes, pigments, optical brighteners and pharmaceuticals.
APPEARANCE
58 - 60 C
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Serious eye damage. Hazard statements: Harmful if swallowed. Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye damage. May cause respiratory irritation.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302-H315-H318-H335
P STATEMENTS
P280-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
41
SAFETY PHRASES
26-39