PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
UN NO.
CLASSIFICATION
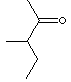
Ketone, Flavoring agent
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.185
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
12 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking (Ketone)
Local:
Ketone is a class of chemical compounds contain the carbonyl group in which the
carbon atom is covalently bonded to an oxygen atom.
Carbonyl groups are:
- Aldehydes (X and Y = H; X = H, Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Ketones (X and Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Carboxylic acids (X = OH, Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Esters (X = O-alkyl or aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Amides (X = NH, N-alkyl, or N-aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Acid halides
- Acid anhydrides
- Lactones
- Lactams
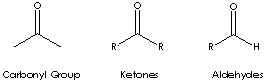
Ketone has the general formula RCOR' where the groups R and R' may be the same or different, or incorporated into a ring (R and R' are alkyl, aryl, or heterocyclic radicals). The simplest example, R and R´ are methyl group, is acetone (also called 2-propanone, CH3COCH3) which is one of the most important ketones used in industry (low molecular weight ketones are general purpose solvents.) In the IUPAC system, the suffix -one is used to describe ketone with the numbering of the carbon atom at the end that gives the lower number. For example, CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3 is named 3-hexanone because the whole chain contains six carbon atoms and the oxygen is connected to the third carbon from the lower number. There are aromatic ketones of which acetophenone and bezophenone are examples. Ketones can be made by the oxidation of secondary alcohols and the destructive distillation of certain salts of organic acids. In addition to as polar solvents, ketones are important intermediates in the syntheses of organic compounds such as alkoxides, hydroxyalkynes, imines, alcohols (primary, secondary as well as tertiary), acetals, thioacetals, phosphine oxides, geminal diols, hydrazones, organic sulfite and cyanohydrins. Methyl Isopropyl Ketone is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
APPEARANCE
95.0% min
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
0.81 - 0.816
BOILING POINT
116 - 118 C