4-NITROBENZONITRILE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
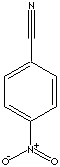
C7H4N2O2
148.12
LD50 orl-rat 30 mg/kg
p-Cyanonitrobenzene; p-Nitrobenzonitrile;
4-Cyanonitrobenzene; 4-Nitrobenzonitrilo (Spanish);
CLASSIFICATION
Pharmaceutical Intermediate
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Yellow solid
146 - 149 C
Insoluble
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
- Michael addition
- Reduction
- Henry Reaction (Nitro-aldol reaction)
- Nef reaction
- O-Alkylation
- Cycloaddition
- Substitution, Elimination, Conversion reaction
- Alkylation, Acylation, and Halogenation
Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general formula RC��N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound) excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O. Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid. The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl derivatives from the isomer, HN+��C-. Sodium cyanide, NaCN; potassium cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or prussic) acid, HCN are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides resemble chlorides in many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including;
- Extraction solvent for fatty acids, oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons
- Solvent for spinning and casting and extractive distillation based on its selective miscibility with organic compounds.
- Removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic alcohols
- Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic salts
- Recrystallization of steroids
- Parent compound for organic synthesis
- Solvent or chemical intermediate in biochemistry ( pesticide sequencing and DNA synthesis)
- High-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis
- Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex catalysts
- Stabilizer for chlorinated solvents
- Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and pharmaceuticals
Benzonitrile, derived mainly from benzoic acid reaction with lead thiocyanate by heating, is a clear liquid; boils at 191 C; It reacts violently with strong acids to produce toxic hydrogen cyanide. It decomposes on heating producing very toxic fumes, hydrogen cyanide, nitrous oxides. Benzonitrile is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyestuffs and rubber chemicals through the reactions of alkylation, condensation, esterification, hydrolysis, halogenation or nitration. Benzonitrile and its derivatives are used in the manufacture of lacquers, polymers and anhydrous metallic salts as well as intermediates for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic chemicals.
99% min
146-149 C
6.1 (Packing Group: II)
3276