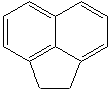
ACENAPHTHENE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
83-32-9
Naphthyleneethylene; Periethylenenaphthalene;
Acenafeno (Spanish); 1,2-Dihydroacenaphthylene; 1,8-Dihydroacenaphthalene; 1,8-Dihydroacenaphthylene; Ethylenenaphthalene; 1,8-Ethylenenaphthalene;
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
93 - 95 C
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
125 C
APPLICATIONS
Acenaphthene, (ethylene-bridged three-ring) unsaturated hydrocarbon derived from naphthalene, is used as an intermediate for 1,8 naphthalic acid, dyes, pharmaceuticals, insecticide, fungicide, herbicide and plant growth hormones. It is used to manufacture plastics and as an agent for inducing polyploidy.
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
91 C min
ASH
0.2% max
3077
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF PAHs
- Acenaphthene: Intermediate for naphthalic acids, naphthalic anhydride (intermediate for pigments) and for acenaphthylene (intermediate for resins); Intermediate for dyes, soaps, pigments, pharmaceuticals, insecticide, fungicide, herbicide and plant growth hormones. It is used to manufacture plastics and as an agent for inducing polyploidy.
- Acridine: Dye and pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Anthracene: Its oxidation yields anthraquinone, the parent substance of a large class of dyes and pigments; .diluent for wood preservatives; scintillant (for detection of high-energy radiation)
- Fluoranthene: manufacturing fluorescent and vat dyes, pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- Fluorene: basic subsance for production of dyes, pigments, pesticides, thermoset plstic and pharmaceuticals; manufacturing fluorenone (mild oxidizing agent)
- Naphthalene: In the production of phthalic anhydride, carbaryl insecticide, beta-naphthol, tanning agents, moth repellent, and surfactants - naphthalene: main use: production of phthalic anhydride (intermediate for polyvinyl chloride plasticizers); also, production of azo dyes, surfactants and dispersants, tanning agents, carbaryl (insecticide), alkylnaphthalene solvents (for carbonless copy paper), and use without processing as a fumigant (moth repellent)
- Phenanthrene: manufacturing phenanthrenequinone (intermediate for pesticides); manufacturing diphenic acid (intermediate for resins)
- Pyrene: manufacturing perinon pigments
- Quinoline: solvent for resins & terpines; decarboxylation agent; parent compound to make drugs, fungicides, biocides, alkaloids, dyes, rubber chemicals and flavoring agents
Precise PAHs, specific refined products are used also in the field of electronics, functional plastics and liquid crystals. Pharmaceutical and agricultural PAHs obtained coal tar are such materials as indole, indolizine, indene, quinoline, quinalidine, isoquinoline and their derivatives. High boiling-point special solvent are such materials as tetoralin, decaline, methyl-naphthalenes. Coumarins and dihydrocoumarins which can be obtained coal tar are PAHs used in perfumery. Thermosensitive paper sensitizer PAHs are such materials as p-benzylbiphenyl and ethylbiphenyl.
|
PARENT COMPOUNDS of PAHs |
|
|
|
|
|
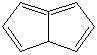
PENTALENE |
INDENE (CAS RN: 95-13-6) |
|
|
|
|
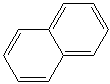
NAPHTHALENE (CAS RN: 91-20-3) |
AZULENE (CAS RN: 275-51-4) |
|
|
|
|
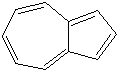
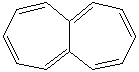
HEPTALENE |
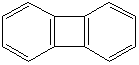
BIPHENYLENE (CAS RN: 259-79-0) |
|
|
|
|
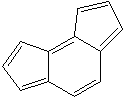
as-INDACENE |
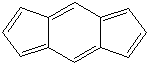
s-INDACENE |
|
|
|
|
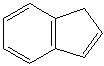
ACENAPHTHALENE (CAS RN: 83-32-9) |
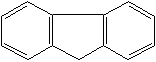
FLUORENE (CAS RN: 86-73-7) |
|
|
|
|
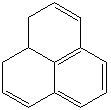
PHENALENE (CAS RN: 203-80-5) |
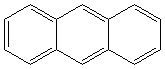
ANTHRACENE (CAS RN:120-12-7) |
|
|
|
|
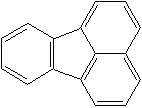
FLUORANTHENE (CAS RN: 206-44-0) |
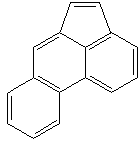
ACEPHENANTHRYLENE |
|
|
|
|
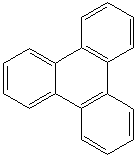
TRIPHENYLENE (CAS RN: 217-59-4) |
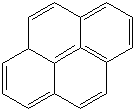
PYRENE (CAS RN: 129-00-0) |
|
|
|
|
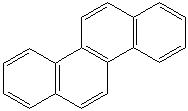
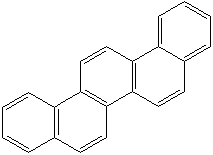
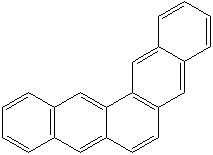
CHRYSENE (CAS RN: 218-01-9) |
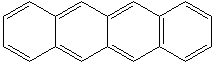
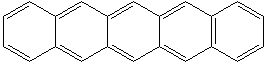
NAPHTHACENE (CAS RN: 92-24-0) |
|
|
|
|
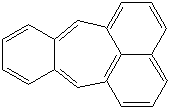
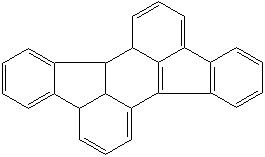
PLEIADENE (CAS RN: ) |
PICENE (CAS RN: 213-46-7) |
|
|
|
|
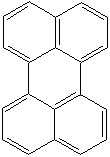
PERYLENE (CAS RN: 198-55-0) |
PENTAPHENE (CAS RN: 222-93-5) |
|
|
|
|
PENTACENE (CAS RN: 135-48-8) |
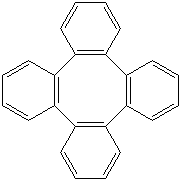
TETRAPHENYLENE (CAS RN: 212-74-8) |
|
|
|
|
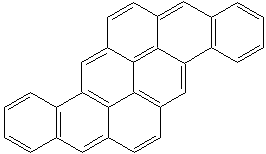
RUBICENE (CAS RN: 197-61-5) |
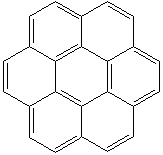
CORONENE (CAS RN: 191-07-1) |
|
|
|
|
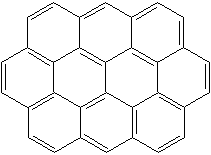
PYRANTHRENE (CAS RN: 191-13-9) |
OVALENE (CAS RN:190-26-1) |