PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
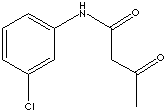
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
131 - 134 C
AUTOIGNITION
460 C
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
FLASH POINT
176 C
APPLICATIONS
Acetoacetates have a reactive hydrogen atom on the carbon alpha to both carbonyl groups. It undergoes Knoevenagel condensation reaction as a reactant to forms a large class of target products including amino acids, drugs, colorants, lacquers, perfumes, and plastics. Alone, it is used as a flavoring agent and a solvent. Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition of a reactive hydrogen atom at 1,3-diketone compounds to a carbonyl group, followed by an dehydration reaction. 1,3-Diketone compounds (beta-ketones) include malonic acid, diethyl malonate, Meldrum's acid, and acetoacetic acid derivatives.
APPEARANCE
0.3% max