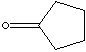| Cyclopentane is the five-membered alicyclic hydrocarbon consisting of five
carbon atoms linked to each other to form a ring, with each carbon atom bearing
two hydrogen atoms, C5H10; melting point -94 C and boiling point 49 C. A cyclic
compound is an organic compound that contains one or more closed rings of carbon
atoms. The term alicyclic refers to cyclic compound that behaves chemically like
aliphatic compounds (open-chain), which means the exclusion of carbocyclic
compounds of aromatic rings with an array of π-electrons characteristic.
Cyclopentane is a colorless, highly flammable, mobile liquid with a pungent
odor. It is insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol, ether, and almost organic
solvents. Cyclopentane is present in crude petroleum. But most of quantity is
converted to aromatics which has better combustion properties to be used in
fuel. Naphthenic acid obtained as a by-product of petroleum refining is
believed to have cyclopentane ring mainly. Cyclopentane consumption is linked
almost entirely to the production of synthetic resins and rubber adhesives.
Cyclopentane is used as a solvent, oil extractant, paint and varnish remover,
dry cleaning material, and in solid fuels. Cyclopentane is used as a chemical
intermediate to produce target molecules. Cyclopentane structure is found in
steroids. Cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene is an example. Alicyclo hydrocarbon
is one of the major skeleton in nature. Cyclopentane derivatives can be used for
the synthesis of fungicides, pharmaceuticals, dyes, herbicides, plant growth
regulator, plasticizers, rubber chemicals, cycloamines and other organic
compounds. Cyclopentanone
can be used as a solvent and intermediate for the synthesis
of insecticides, rubber chemicals, flavor
and fragrance chemicals.
It is used in manufacturing pharmaceuticals and biological
biologically
active compounds. |
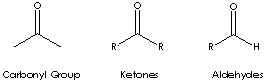
| Ketone is a class of chemical compounds contain the carbonyl group in which the
carbon atom is covalently bonded to an oxygen atom.
Carbonyl groups are:
- Aldehydes (X and Y = H; X = H, Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Ketones (X and Y = alkyl or aryl)
- Carboxylic acids (X = OH, Y = H, alkyl, or
aryl)
- Esters (X = O-alkyl or aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Amides (X = NH,
N-alkyl, or N-aryl; Y = H, alkyl, or aryl)
- Acid halides
- Acid anhydrides
- Lactones
- Lactams
Ketone has the general formula
RCOR' where the groups R and R' may be the same or different, or incorporated
into a ring (R and R' are alkyl, aryl, or heterocyclic radicals). The simplest
example, R and R´ are methyl group, is acetone (also called 2-propanone,
CH3COCH3) which is one of the most important ketones used in industry (low
molecular weight ketones are general purpose solvents.) In the IUPAC system, the
suffix -one is used to describe ketone with the numbering of the carbon atom at
the end that gives the lower number. For example, CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3 is named
3-hexanone because the whole chain contains six carbon atoms and the oxygen is
connected to the third carbon from the lower number. There are aromatic ketones of which acetophenone and bezophenone are examples. Ketones can be made by the
oxidation of secondary alcohols and the destructive distillation of certain
salts of organic acids. In addition to as polar solvents, ketones are important
intermediates in the syntheses of organic compounds such as alkoxides,
hydroxyalkynes, imines, alcohols (primary, secondary as well as tertiary),
acetals, thioacetals, phosphine oxides, geminal diols, hydrazones, organic
sulfite and cyanohydrins.
|