PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
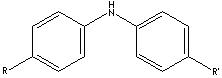
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
brown flakes
213 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
http://ksundaram.tripod.com/
...The
Primary antioxidants consist mainly of hindered phenols and hindered
aromatic amines. They scavenge and destroy the chain propagating
peroxy and alkoxy radicals before they can react with the polymer.
These materials contain hydrogen atoms that can be easily donated
to the chain-propagating peroxy, alkoxy,and hydroxy radicals. The
alkoxy and hydroxy radicals are converted to alcohols and water,
respectively, which are inert and do not hamper polymer stability.
The antioxidant radicals formed are stable and do not abstract more
hydrogens from polymer. A typical primary antioxidant of the hindered
aromatic amine variety is AO-TMQ (Polymerized 1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline)....
The
amine antioxidants are generally more powerful than the hindered
phenols. This is due to a cyclic process which the amine antioxidant
undergoes in which a nitroxyl radical is regenerated and consumes
more radicals. A drawback of the aminic AO��s is that they are oxidized
to products which are more discoloring and staining than their hindered
phenol counterparts. AO-1010 is exceptional among hindered phenolic
AO��s. It has one of the highest molecular weights in its class
and is non-staining, nondiscoloring, and effective in non-black,
colorable rubber compounds.......
http://www.sciencedirect.com/
Antioxidants can be divided into two broad classes, primary and secondary,
depending upon their mode of action. The most broadly used primary antioxidants
are hindered phenolics. Phenolic antioxidants have traditionally been based on
2,6-di-t-butyl-4-methylphenol (BHT). This functional moiety has been
incorporated into larger molecules affording products with lower volatility or
greater polymer compatibility. More recently, molecules have been introduced
which vary in steric hindrance about the phenol and also the way in which
multiple phenol functional groups are linked to form larger molecules. This has
led to structures which have lower colour contribution. Surprisingly, in some
cases these molecules have shown higher levels of efficiency relative to other
antioxidants with similar phenol/molecular weight ratios. This has included
enhanced levels of synergism with secondary antioxidants. An attempt is made to
correlate structural features of these molecules to the enhanced performance
and/or lower colour.
APPEARANCE
brown flakes
10% max
MELTING POINT
84 C
HEAT LOSS
0.5% max
ASH
0.3% max
INSOLUBLES
0.3% max (in acetone)