INDIGO
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
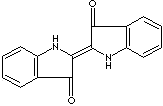
CLASSIFICATION
Coloring Agent, Redox Indicators, Stains and Dyes
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Health Hazard: 2, Fire: 0, Reactivity Hazard: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indigo, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indigo_dye
http://www.madehow.com/
Indigo, or indigotin, is a dyestuff originally extracted from the varieties
of the indigo and woad plants. Indigo was known throughout the ancient world for
its ability to color fabrics a deep blue. Egyptian artifacts suggest that indigo
was employed as early as 1600 B.C. and it has been found in
Africa, India, Indonesia, and China. The dye imparts a brilliant blue hue to fabric. In the dying process, cotton and linen threads are usually
soaked and dried 15-20 times. By comparison, silk threads must be died over 40
times. After dying, the yarn may be sun dried to deepen the color. Indigo is
unique in its ability to impart surface color while only partially penetrating
fibers. When yarn died with indigo is untwisted, it can be seen that the inner
layers remain uncolored. The dye also fades to give a characteristic wom look
and for this reason it is commonly used to color denim. Originally extracted
from plants, today indigo is synthetically produced on an industrial
scale.....
http://faculty.bennington.edu/
Indigo
is a vat dye, meaning that the colorant itself (that is, pure indigo)
is not soluble in water and therefore cannot be used directly to
color fabric. This is because a dye must penetrate the fibers of
a material in order to produce an effective color; they cannot be
simply applied to the surface like a paint. So to use indigo to
dye fabrics, it must in a converted to a compound that readily dissolves
in water. In traditional dyeing procedures, the reaction to produce
the soluble form of the dye took place in open vats, hence the term,
vat dye....
APPEARANCE
CONTENT
94.0% min
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
1.0% max
MOISTURE
0.8% max
IRON
0.5% max
PARTICLE SIZE
96.0% min (60 mesh)
3079
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319-H335
P STATEMENTS
P261-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36