PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.931
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
107 C
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
WATER
0.5% max
ANILINE
Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/22, Safety Phrases: 28A/37/45
|
|
|
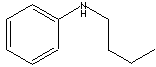
| N-BUTYLANILINE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1126-78-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 214-425-6 | |
| FORMULA | C6H5NH(CH2)3CH3 | |
| MOL WT. | 149.23 | |
| H.S. CODE |
| |
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 1620 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Phenyl N-Butyl Amine; N-Butyl-Benzenamine; | |
| 4-(Phenylamino)butane; N-Butylbenzenamine; N-(n-Butyl)aniline; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | light yellow liquid | |
| MELTING POINT | -12 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 236 - 242 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.931 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 5.1 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 3; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.5320 | |
| FLASH POINT |
107 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions (light sensitive) | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| One of the most important aromatic amines is aniline; pale brown liquid boiling at 184 C, melting at -6 C. Aniline is obtained commercially from chlorobenzene by heating with ammonia in the presence of copper catalyst or from a product of coal tar (nitrobenzene) through the reduction reaction. Aniline is the starting material in the dye manufacturing industry and as in the manufacture of others. Aniline is converted into sulfanilic acid which is the parent compound of the sulfa drugs. Aniline and its derivatives are also important in the manufacture of rubber-processing chemicals, antioxidants and varnishes. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
light yellow liquid | |
| CONTENT |
99.0% min | |
|
WATER |
0.5% max | |
|
ANILINE |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 180kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 2738 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/22, Safety Phrases: 28A/37/45 |
||
|
|
|