| CAS
NO. |
92-82-0 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
202-193-9 |
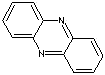
| FORMULA |
C6H4N2C6H4 |
| MOL
WT. |
180.21 |
| H.S.
CODE |
|
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
Dibenzopyrazine; Acridizine;
吩嗪; 9,10-Diazaanthracene; |
| Azophenylene;
Dibenzo-p-diazine; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
yellow
to brown needle crystals |
| MELTING
POINT |
174
- 177 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
360
C |
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Slightly
soluble (soluble in alcohol, ether, benzene) |
| AUTOIGNITION
|
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
6.21 |
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health:
1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
Phenazine is a pyrazine class polycyclic compound which have two nitogen atoms
in the ring. Nitrogen atoms in polycyclic compound form chromophore groups.
Phenazine is a yellowish crystals; melting point 170C; slightly soluble in
water, soluble in alcohol and ether. It is the parent compound of members of
azine dyes such as nigrosines,indulines, and safranine. Nitrogen in phenazine plays an important role in biological research and drug manufacturing
industry including the preparation of antibiotics, anthelmintic, antiallergenic,
antihistamic, antiemetic and antimigraine agents. The phenazine ring and
phenazine derivatives are important cyclic components in industrial field as raw
materials for pesticides, flavourings and perfumery. Phenazine is a metal chelator. It is used in
metallocene industry for the application including;
- Coordination of
organometallic-complexes
- Redox mediators in biosensor
- Catalysts for the
oxidative organic synthesis
- Molecular chemistry
- Disease diagnosis and
treatment
- Water treatment
- Photolysis chemistry
- Microbiology
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
yellow
to brown needle crystals |
| PURITY |
99.0%
min
|
| MELTING
POINT |
174
- 177 C |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 40, Safety
Phrases: 45 |
