PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
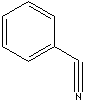
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
72 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids,
oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons
· Solvent for spinning and casting and
extractive distillation based on its selective miscibility with organic
compounds.
· Removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic
alcohols
· Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic
salts
· Recrystallization of steroids
·
Parent compound for organic
synthesis including ketones and amines
· Solvent or chemical intermediate in biochemistry ( pesticide
sequencing and DNA synthesis)
·
High-pressure liquid chromatographic
analysis
· Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex
catalysts
· Stabilizer for chlorinated
solvents
· Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and
pharmaceuticals
Benzonitrile, derived mainly from benzoic acid reaction with lead thiocyanate by heating, is a clear liquid; boils at 191 C. It reacts violently with strong acids to produce toxic hydrogen cyanide. It decomposes on heating producing very toxic fumes, hydrogen cyanide, nitrous oxides. Benzonitrile is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyestuffs and rubber chemicals through the reactions of alkylation, condensation, esterification, hydrolysis, halogenation or nitration. Benzonitrile and its derivatives are used in the manufacture of lacquers, polymers and anhydrous metallic salts as well as intermediates for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other organic chemicals.
http://www.chem.mq.edu.au
Benzonitriles
are of considerable interest for organic chemistry as integral part
of dyes, herbicides, agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and natural
products. The nitrile group also serves as an important intermediate
for a multitude of possible transformations into other functional
groups. As an example the synthesis of Fluvoxamine. Here, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile,
which is available from 4-chlorobenzotrifluoride by nickel-catalyzed
cyanation on ton-scale, serves as an intermediate. Benzonitriles
themselves are also of significant interest, e.g., as substructures
in biologically active agents. Two selected examples of pharmaceuticals
containing an aromatic nitrile as part of the molecule are shown
along with their names, producers, and effects. In case of
biologically active benzonitrile derivatives another aspect is worth
noting. By applying transition metal-catalyzed cyanation of aryl
halides using K11CN, K13CN or K14CN isotope labelled compounds are
easily accessible [5–9]. The resulting products are used in pharmacokinetic
studies and investigations on the metabolism of pharmaceuticals.....
APPEARANCE
99.5% min
COLOR, APHA
30 max
2224