PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
pale yellow liquid
AUTOIGNITION
550 C
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
FLASH POINT
33 C
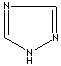
- Triazole: An analog of imidazole. It has three nitrogen atoms and two carbon atoms at nonadjacent positions in the ring system.
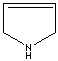
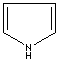
- Pyrrole: An analog of imidazole. It has only one nitrogen atom in the ring system. Pyrrole ring system is involved in coloured products (green pigment, chlorophyll; red, hemoglobin; , blue, indigo) in nature.
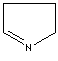
- Pyrroline: A pyrrole in which one of the two solid bonds are hydrogenated.
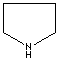
- Pyrrolidine: The saturated tetrahydropyrrole, a part of the structures of amino acids (proline, hydroxyproline and hygrine).
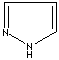
- Pyrazole: 1,2-Diazole (Imidazole isomer). The nitrogen positions are 1 and 2. It is not found in nature
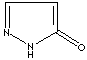
- Pyrazolone: Pyrazole analog with ketone group at 5 position
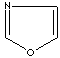
- Oxazole: an analog of imidazole. The nitrogen atom in position 1 is replaced by oxygen.
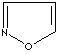
- Isoxazole: an analog of pyrazole. The nitrogen atom at position 1 is replaced by oxygen.
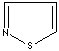
- Isothiazole:an analog of pyrazole. The nitrogen atom at position 1 is replaced by sulfur.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,2,4-Triazole |
Pyrrole |
1-Pyrroline |
3-Pyrroline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pyrrolidine |
Pyrazole |
Pyrazolone |
Oxazole |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isoxazole |
Isothiazole |
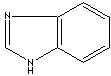
Benzimidazole |
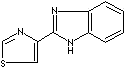
Thiabendazole |
APPEARANCE
pale yellow liquid
99.0% min
WATER