PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
Anthraquinone dye
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
orange or red crystalline powder
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Quinizarin
Google Scholar Search - Quinizarin
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Quinizarin
PubChem Compound Summary - Quinizarin
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Quinizarin
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Quinizarin
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Quinizarin
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous
Substances Data Bank - Quinizarin
Local:
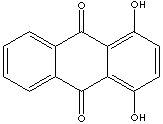
Anthraquinone, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon containing two opposite carbonyl groups (C=O) at 9,10 position, is yellow or light gray to gray-green crystal powder; insoluble in water. , In nature, it occurs in plants (aloe, cascara sagrada, senna, and rhubarb), fungi, lichens, and insects as a parent material for coloring of yellow, orange, red, red-brown, or violet. It is commercially produced by several ways including by oxidation of anthracene with chromic acid, the condensation of benzene and phthalic anhydride, followed by dehydration for cyclization, and diene Diels-Alder reaction. Anthraquinone is the most important quinone derivative of anthracene as the parent substance of a large class of dyes and pigments. One of the oldest mordant dye, alizarin, is the anthraquinone derivative. Anthraquinone is a starting material for the production of coloring compounds, antioxidants, and polymerization inhibitors. Its derivatives are widely used as intermediates for dyes, pigments, photographic chemicals, and paints. Anthraquinone is used in paper industry as a catalyst to increase the pulp production yield and to improves the fiber strength through reduction reaction of cellulose to carboxylic acid. Natural anthraquinones have cathartic properties. Anthraquinones derivatives are also used in manufacturing drugs. Mitoxantrone, an antineoplastic is an example. Quinizarin, 1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of indanthrene and alizarin dyestuffs. It is also used to form lakes with calcium, barium, and lead. Alizarin is 1,2-Dihydroxyanthraquinone. Chrysazin is 1,8-Dihydroxyanthraquinone. Chrysazin is called d anthron when used as a cathartic. It was used as a stimulant laxative to treat constipation. But it is no longer widely used due to its potential to cause cancer. 2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone is called anthraflavic Acid. Dihydroxyanthraquinone molecules include:
|
|
APPEARANCE
orange or red crystalline powder
95.0% min
MELTING POINT
194 - 195 C
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Eye irritation, Skin sensitization
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H317
P STATEMENTS
P280
RISK PHRASES
36 Irritating to eyes
43 May cause sensitisation by skin contact
SAFETY PHRASES
24 Avoid contact with skin