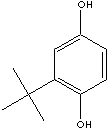
| tert-BUTYLHYDROQUINONE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. |
1948-33-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 217-752-2 | |
| FORMULA | (CH3)3CC6H3(OH)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 166.22 | |
| H.S. CODE |
2907.29.0090 | |
| TOXICITY | Oral, rat: LD50: 700 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | tert-Butyl-1,4-benzenediol; 2-tert-Butylhydroquinone; | |
| TBHQ; 2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-1,4-benzenediol; Mono-tert-butylhydroquinone; Mono-tert-butylhydroquinone; MTBHQ; Mono-tertiarybutylhydroquinone; 2-tert-Butyl-1,4-benzenediol; 2-tert-Butylhydroquinone; 2-tert-Butylhydrochinon (German); 2-terc-butilhidroquinona (Spanish); 2-tert-butylhydroquinone (French); | ||
|
SMILES |
C(c1c(ccc(c1)O)O)(C)(C)C | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antioxidant, Hydroquinone |
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to light tan crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 126.5 - 128.5 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 273 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
| FLASH POINT |
43 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS |
||
|
Antioxidant is a substance added in small quantities to hydrocarbons which are
susceptible to oxidation, such as rubbers, plastics, foods, and oils to inhibit
or slow oxidative processes, while being itself oxidized. Antioxidants work in
two different ways. In primary antioxidants (also called free-radical
scavengers), antioxidative activity is implemented by the donation of an
electron or hydrogen atom to a radical derivative. These antioxidants are
usually hindered amines (p-Phenylene diamine, trimethyl dihydroquinolines,
alkylated diphenyl amines) or substituted phenolic compounds with one or more
bulky functional groups such as a tertiary butyl at 2,6 position commonly.
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is a common example of hindered phenolic
antioxidant. The reaction rate, or carbocation stability, in SN1 mechanism is 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3
(no SN1) so, tertiary alkyl moiety exists in lots of phenolic antioxidant
compounds. Primary antioxidants are free radical scavengers which combine with
peroxy radicals and break autocatalytic cycle. In secondary antioxidants ( also
called peroxide decomposers), activity is implemented by the removal of an
oxidative catalyst and the consequent prevention of the initiation of oxidation.
Examples of peroxide decomposer type of antioxidant are trivalent phosphorous
and divalent sulfurcontaining compound such as sulfides, thiodipropionates and
organophosphites. Synergistic effect is expected when primary antioxidants are
used together with secondary antioxidants as primary antioxidants are not very
effective against the degradation by UV oxidation. Sometimes, chelating agents
are added to scavenge metal impurities which can initiate decomposition.
Tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) is a white, crystalline solid having a characteristic odor. It is practically insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and in ether. TBHQ is a general purpose antioxidant used to preserve various oils, fats and food items by retarding their oxidative deterioration. It is used in formulating varnish, lacquer, resins and oil field additives. It is used a fixative in perfumery to reduce the evaporation rate and improve stability. It is used as a stabilizer to inhibit the auto-polymerization of organic peroxides. Wikipedia Linking:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tert-butylhydroquinone http://mirror.switch.ch/ http://www.adeka.co.jp/ |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to light tan crystalline powder | |
| ASSAY (G.C) | 99.0% min | |
|
IMPURITY |
0.1%
max (Hydroquinone) | |
| MELTING POINT | 126.5 - 128.5 C | |
| TOLUENE | 0.0025% | |
| XYLENE | 0.0025% | |
| UV ABSORBANCE | 280-289nm 0.15abs/cm 290-299nm 0.12abs/cm 300-359nm 0.08abs/cm 360-400nm 0.02abs/cm | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in fiber drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22, Safety Phrases: 26-28A | ||
| DESCRIPTION OF QUINONE | ||
|
Quinone is a group of aromatic compounds containing two opposite carbonyl groups (C=O) and the other two pairs of carbon atoms linked by vinylene group(-CH=CH) in a six-membered unsaturated ring. The carbonyl groups are located in different rings and form various chemical structures which offer important roles to colours. Quinones are used in photography and dye manufacture. Quinones occur benzoquinones, naphthoquinones, anthraquinones, and polycyclic quinones. Though quinones are found in plants and in a few animals, they usually are prepared by oxidation of aromatic amines, polyhydric phenols, and polynuclear hydrocarbons.The reduction of quinone to the corresponding dihydroxy form is an important characteristic reaction. In acidic solution, p-benzoquinone is reduced reversibly to hydroquinone. The so-called quinhydrone electrode, containing equimolar solution of quinone and hydroquinone, is used to determine hydrogen ion concentrations depends on the oxidation-reduction reactions. Hydroquinone and its derivatives used principally in photographic dye chemicals, in medicine, as an antioxidant, and in paints, varnishes, and motor fuels and oils. Hydroquinone and certain derivatives are also used as polymerization inhibitors by direct reacting with peroxy-free radical to tie up free radicals. |
||