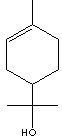
TERPINEOL
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
Oral rat LD50; 5170 mg/kg
CLASSIFICATION
Flavor, Monoterpene
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
18 C
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
95 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Turpentine is the oleoresin obtained from species of Pinus. It is composed of volatile turpentine oils. Terpin is a product obtained by the action of nitric acid on turpentine oil and alcohol, with general formula CH3(OH)C6H9C(CH3)2OH. Terpin is slightly soluble in water, soluble in alcohol and ether; melting at 116 C. The hydrate form of terpin is used as an expectorant. Terpineol is a product of dehydrated 1,8-terpin which has lilac odor; boiling at 214 - 224 C, melting point 18 C. Terpineol is used in fragrance compositions in disinfectants, polishes and household products, and also as an intermediate in the production of very high purity alpha-terpineol. Three isomeric terpineols exit, called alpha-, beta-, and gamma-terpineol, differing by the location of the solid bond and hydroxy group. Beta form does not exit in nature.
The term "Tea Tree" includes species of the genus Leptospermum and Melaleuca, the latter covering more than 200 species (Byres 1986) of the family Myrtaceae. The most common and economically important member of this group is the Australian Tea Tree, Melaleuca alternifolia (Maid. and Bet.) Cheel (syn. M. linariifolia var. alternifolia Maid. and Bet.). Its native habitat is restricted to the swamps and water-courses of the subtropical coastal region of New South Wales in Australia between 32° and 27°S, growing best in high-rainfall areas, or low rain-fall areas with irrigation. It is a small tree 5-7m, naturally forming impenetrable thickets, and being coppiced easily. As one travels from South to North of its natural habitat, so the leaf oil composition changes, being 1,8-cineole rich in the South, and high terpinen-4-ol, low 1,8-cineole in the North. Leaf oil content can range from 0.5 to 3.0%, but yield from traditional design waterdistillation is 1%, unless more modern still design is used. In the last few years the tree has also been successfully cultured in more diverse locations such as Zimbabwe, Kenya, Vietnam, India, Guatemala and China, among others. (http://www.users.globalnet.co.uk/)
Tea tree oil is the essential oil steam distilled from the Australian native plant, Melaleuca alternifolia. Tea tree oil contains over 100 components, the majority being monoterpene and sesquiterpene hydrocarbons and their alcohols. The antibacterial properties of tea tree oil have now been well documented, and there are susceptibility data on a wide range of bacteria. There is also considerable information identifying the components of tea tree oil active against bacteria and yeasts. Until recently there have only been anecdotal claims about tea tree oil��s anti-inflammatory activity. The only specific report on anti-inflammatory properties of tea tree oil has been of an in vitro study published as an abstract in which the addition of tea tree oil to lipopolysaccharideprimed neutrophils inhibited superoxide release by approximately 85%. The concentration of tea tree oil used was 0.05% v/v.(http://www.burnaid.com/)
Tea Tree Oil is the essential oil extracted by the steam distillation of the foliage of the Melaleuca alternifolia (also known as punktree, paperbark-tree) belong to the family of Myrtaceae. Tea Tree Oil is a combination of more than 100 components, mostly monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes and terpene alcohols. The major component for antimicrobial and antifungal activity is terpinen-4-ol (typically 30-40%). Tea Tree Oil has been used as a general antiseptic for thousands of years. It is being an ingredient in skin care, health care, cosmetic and toiletry products due to its benefits of anti fungal, antiseptic, germicidal and anti-bacterial properties. It is also used as a natural cleaner, pharmaceuticals, veterinary and disinfectant in the household product.
Terpinen-4-ol is a terpene alcohol found in long leaf pine and petitgrain oil. Hydoxy group position is differ form alpha-terpineol. It is the main component of tea tree oil showing the antibacterial and antifungal activity. It also occur as the highest concentration component in the essential oil of evergreen tree Myristica fragrans. can be isolated directly from a variety of sources or can be manufactured from the more readily available terpene (alpha-pinene). but It is used as an antiseptic and in the manufacture perfume. There are two enantiomers with characteristic odor properties. Terpineol has a pleasant odor similar to lilac.Terpinolene is obtained by distillation fraction of pine oil. Terpinolene is converted to Terpinen-4-ol under hydrolysis reaction. Commercial terpinolene contains cyclic isomers. It is used as a solvent and used in fragrance industry for pine odor in cleaners, deodorizers, masking agents.
|
|
APPEARANCE
REFRACTIVE INDEX
COLOR, APHA
30 max
REFRACTIVE INDEX
PRICE INFORMATION