PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
112-57-2
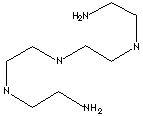
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
0.998
321 C
139 C
APPLICATIONS
Diethylenediamine is the simplest cyclic ethyleneamine (C-4), called piperazine. It has two secondary amine groups in cyclic system. It is a deliquescent crystalline compound melting at 105 C; soluble in water, alcohol, glycerol, and glycols. It is used as a main ingredient of anthelmintics and psychoactive drugs. Aminoethylpiperazine is also a member of C- 6 cyclic ethyleneamine which has aminoethyl attached to a nitrogen in piperazine. Accordingly, it has one primary, one secondary, and one tertiary nitrogen atom. It is used in the synthesis of catalysts, epoxy curing agent, and corrosion inhibitors. Aminoethylethanolamine (AEEA) is an analogue of diethylenetriamine. A hydroxyl group replace for an primary amine group. AEEA has one primary amine, one secondary amine, and one primary hydroxyl group. AEEA is a useful intermediate in the production of surfactants, chelating agents, and curing agents. Other branched or cyclic ethylenediamines include N,N'-Bis-(2-aminoethyl)piperazine) [CAS #: 6531-38-0], N-[(2-aminoethyl)2-aminoethyl]piperazine) [CAS #: 24028-46-4], tris(2-aminoethyl)amine) [CAS #: 4097-89-6].
Ethylenediamines are produced by the reaction of aqueous ammonia with 1,2-dichloroethane. This process yields the mixture of polyamines in the form of hydrochloride salts. The next step is neutralisation of the salts with aqueous caustic soda to separate free amines. The individual free amines are isolated by fractional distillation. Ethylenediamines are capable of entering into a variety of reactions because of their combination of reactivity, basicity, and surface activity and of the basic functionality of the nitrogen atom. They are therefore important intermediates for a wide variety of chemical syntheses. Examples of products obtained by reacting amines are as follows:
- with carboxylic acid dericatives (acids, esters, anhydrides, or acyl halides): amides and amidoamines
- with fatty acid: imidazoline
- with cyanides or nitriles: amidoamines, polyamides, imidazolines
- with urea: substituted urea and ammonia
- with ethyleneimines: hydroxyalkyl amine derivatives
- with aliphatic alcohols and glycols: alkylated ethyleneamines or cyclic ethyleneamines
- with alkyl or aryl halides: substituted amines
- with aliphatic aldehydes: substituted imidazolidines
- with carbon disulfide: thiocarbamates
- with carbon dioxide: carbamate
- with inorganic acids: water soluble salts
Ethylenediamine is used as a very important bidentate ligand forming chelate agents. The main application is to produce chelating agents such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). It is used in the manufacture of carbamate fungicides, surfactant and dyes. It is useful also in manufacturing accelerator or curing agent in epoxy industry. Additional applications include manufacturing photography development chemicals and cutting oils, bleaching activators for washing powders especially at low temperature, lubricant for plastics and polyamide process, and fuel additives.
Diethylenetriamine is a yellow, hygroscopic liquid; boiling point of 206 C; soluble in water and hydrocarbons. It is used as a solvent for sulfur, acidic gas, resin and as a fuel and oil field component. It is used as an Intermediate for organic synthesis (modified polyamides, corrosion inhibitors, fuel additives, epoxy curing agents, fabric softeners and adhesion promoters) and saponification agent for acidic materials.
Triethylenetetramine is a clear to yellowish oily liquid; melting point 12 C, boiling point 280 C. It is miscible with water and the solution is alkaline ( (pH 10 at 10% solution). It reacts with ketones, halogenated hydrocarbons, nitriles, epoxides, and with strong oxidants. Commercial triethylenetetramine is a mixture of linear TETA (typically 60%) and branched or cyclic TETA such as N,N'-Bis(2-aminoethyl)piperazine, N-[1-(2-piperazin-1-yl-ethyl)]ethane -1,2-diamine, tris-(2-aminoethyl)-amine. TETA and its derivatives are used as an epoxy curing agent. Their applications are similar to those of ethylenediamine and diethylenetriamine. Tetraethylenepentamine and pentaethylenehexamine are ethylenediamine family products which have similar in structure but containing extra ethylamine. Due to structural similarity, TEPA and PEHA have almost similar chemical properties and the same applications.
End uses of ethylenediamine family products include:
- Dispersant-detergent
- Modified Polyamides
- Fabric Softeners
- Ore Flotation Agents
- Emulsifiers
- Corrosion Inhibitors
- Adhesives
- Binding Agents
- Chelating Agents
- Bleach Activators
- Epoxy Curing Agent
APPEARANCE
95.0% min
COLOR, GARDNER
5 max