| CAS
NO. |
2835-68-9 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
220-612-3 |
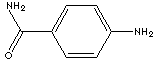
| FORMULA |
H2NC6H4CONH2 |
| MOL
WT. |
136.15 |
| H.S.
CODE |
|
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
p-Aminobenzoic acid amide; 4-Aminobenzamide; |
|
p-Carbamoylaniline; 4-AB; 4- aminobenzamid; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to light tan powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
181-183 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
|
| AUTOIGNITION
|
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
|
| REFRACTIVE
INDEX |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
p-Aminobenzamide
is used as an intermediate in the manufacture
of pigments, dyes and other organic
compounds.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to light tan powder |
| ASSAY |
98.0%
min |
|
MELTING
POINT
|
180
C min
|
|
WATER
|
0.5%
max
|
|
ASH
|
0.5%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in bag |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF AMIDE |
|
Amide is a group of organic chemicals with the general formula RCO-NH2 such as
acetamide, where 'R' groups range from hydrogen to various linear and ring structures
or a compound with a metal replacing hydrogen in ammonia such as sodium amide,
NaNH2. Amide is formed from of ammonia (NH3) and a carboxylic acid in which a
carbon atom is solid bonded to oxygen and also to an hydroxyl group or by
reaction of an acid chloride, acid anhydride, or ester with an amine. An amide
is hydrolyzed to yield an amine and a carboxylic acid. The reverse of this
process results in the loss of water and is used in nature to link amino acids
to form proteins, the secondary structure of which is due in part to the
hydrogen bonding abilities of amides. Sulfonamides are analogs of amides in
which the atom solid bonded to oxygen is sulfur rather than carbon. Polyamide
is a polymer containing repeated amide groups, as in various kinds of nylon and
polyacrylamides. |
