PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
127 C
APPLICATIONS
NITROBENZENE (also called NITROBENZOL ) is a colourless to pale yellow, oily, highly toxic liquid with the odour of bitter almonds. Nitrobenzene is manufactured commercially by nitration of benzene (also a common air pollutant) using a mixture of nitric and sulfuric acids. Commercially nitrobenzene can be either produced in a batch or by a continuous process. Both batch and continuous processes employing mixed nitric and sulfuric acids are used to make nitrobenzene. The continuous process is favored over the batch process because its production capacity is much larger, it has lower capital costs and it entails more efficient labor usage. Reactors for the continuous process also usually utilized lower nitric acid concentrations, are smaller with more rapid and efficient mixing, and therefore have higher reaction rates. Nitrobenzene undergoes nitration, halogenation, and sulfonation much more slowly than does benzene. It may be reduced to a variety of compounds, depending on the reaction conditions. Most nitrobenzene produced is reduced to aniline; smaller amounts are converted to azobenzene, hydrazobenzene (the intermediate for benzidine), and phenylhydroxylamine. Reduction of both the nitro group and the benzene ring affords cyclohexylamine. Nitrobenzene is used as a mild oxidizing agent in the syntheses of quinoline and fuchsin. There are 16 compounds of chloronitrobenzenes (e.g: three mono- isomeric substances, six di-, four tri-, and two tetra-, as well as penta- chloronitrobenzene). They are produced for industrial uses which are the manufacture of other compounds such as dyes, drugs, pesticides, shoe polish, spray paint, and synthetic rubber.
- o-Chloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 88-73-3)
- m-Chloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 121-73-3)
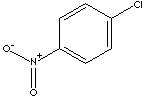
- p-Chloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 100-00-5)
- 2,3-Dichloronitrobenzene; (CAS RN: 3209-22-1)
- 2,4-Dichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 611-06-3)
- 2,5-Dichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 89-61-2)
- 2,6-Dichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 601-88-7)
- 3,4-Dichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 99-54-7)
- 3,5-Dichloronitrobenzene ( CAS RN: 618-62-2)
- 2,3,4-Trichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 17700-09-3)
- 2,4,5-Trichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 89-69-0)
- 2,4,6-Trichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 18708-70-8)
- 3,4,5-Trichloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 20098-48-0)
- 2,3,4,5-Tetrachloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 879-39-0)
- 2,3,5,6-Tetrachloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 117-18-0)
- Pentachloronitrobenzene (CAS RN: 82-68-8)
- Michael addition
- Reduction
- Henry Reaction (Nitro-aldol reaction)
- Nef reaction
- O-Alkylation
- Cycloaddition
- Substitution, Elimination, Conversion reaction
- Alkylation, Acylation, and Halogenation
Nitro compounds are readily reduced into amines when reacted with hydrochloric acid. Aromatic nitro compounds also yield anilines, aromatic amine compounds. Nitro compounds are cleaved into two parts by the addition of a molecule of water to produce carbonyl compounds (aldehydes or ketones). Aromatic nitro compounds undergo nucleophilic substitutions to be replaced by the hydroxide anion, resulting in the creation of phenol compounds and by alkoxy nucleophiles to corresponding ethers.
p-Nitrochlorobenzene is used as an intermediate for organic synthesis; p-nitrophenol, azo dyes and sulfate dyes, pharmaceuticals(such as phenacetin and acetaminophen ) and pesticides (such as nitrofen, parathion) and rubber chemicals
APPEARANCE
CONTENT
98.0% min
ISOMER IMPURITY
2.0% max
MOISTURE
0.2% max
1578