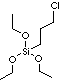|
(3-CHLOROPROPYL)TRIETHOXYSILANE |
| (3-Chloropropyl)triethoxysilane; Triethoxy(gamma-chloropropyl)silane; 3-Chloropropyltriethoxysilane; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
5089-70-3 |
|
EINECS RN |
225-805-6 |
|
FORMULA |
ClCH2CH2CH2Si(OCH2CH3)3 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
240.80 |
|
SMILES |
ClCCC[Si](OCC)(OCC)OCC |
| H.S. Code | 2931.00.9010 |
|
UN NO. |
1993 |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Trialkoxysilane, Chloroalkylsilane, Silane Coupling Agent |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
|
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
clear liquid |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
230 C |
|
DENSITY |
1.002 - 1009 |
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Insoluble |
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.415 - 1.425 |
|
FLASH POINT |
34 C |
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents, Acids. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Hydrogen chloride gas, carbon oxides, oxides of silicon. |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported. |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2. Flammability: 3, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Flammable liquid, Target Organ Effect, Irritant, Carcinogen. Target Organs: Eyes, Skin |
|
EYE |
Causes eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. Causes skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. Causes respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
1993 |
| HAZARD CLASS |
10 |
| PACKING GROUP |
III |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XI |
|
RISK PHRASES |
10-36/37/38 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
16-26-37/39 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
http://www.amchro.com/ |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid |
|
CHLORIDE |
100 ppm max |
|
PURITY |
98.5% min |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|