|
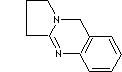
3-DEOXYVASICINE |
| 1,2,3,9-Tetrahydropyrrolo(2,1-b)quinazoline; Deoxypeganin; Deoxypeganine; Desoxypeganine; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
495-59-0, 61939-05-7 (hydrochloride) |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C11H12N2 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
172.23 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white to yellow powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
86 - 87 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides. nitrogen oxides, ammonia |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed |
|
EYE |
|
|
SKIN |
|
|
INGESTION |
|
|
INHALATION |
|
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
T |
|
RISK PHRASES |
23/24/25 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
28-36/37/39-45 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | |
|
The pharmacological activities of vasicine and vasicinone are well known. Recent investigations on vasicine showed bronchodilatory activity comparable to theophylline, both in vitro and in vivo. Both the alkaloids in combination showed pronounced bronchodilatory activity. Vasicine also exhibits strong respiratory stimulant activity. There has also been a report of thrombopoetic4 (platelet-increasing) activity with vasicine. Uterine stimulant activity and moderate hypotensive activity of the alkaloids have been observed. (http://thestar.com.my/) Adulsa(Adhathoda vasica), also known as vasaka, is distributed all over the plains of India & in lower Himalayan ranges, ascending to a height of 1.5 m. The plant has been recommended by Ayurvedic physicians for the management of various types of respiratory disorders. It possesses potent bronchodilatory, expectorant, anti-spasmodic and anti-septic properties. It also possesses significant antimicrobial activity against gingival inflammation and pyorrhea. It has also shown Uterine stimulant activity, moderate hypotensive activity and thrombopoeitic activity. The leaves of the plant contain two major alkaloids called vasicine and vasicinone which are responsible for its medicinal properties. The bronchodilatory & expectorant properties of the leaves are attributed to vasicine. Recent investigations on vasicine showed bronchodilatory activity comparable to theophylline, which is a methylxanthine drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as COPD or asthma. (http://www.associatedcontent.com/) Deoxypeganine (an alkaloid) present in Peganum harmala has been reported to be helpful in treating Alzheimer dementia. Deoxypeganine has been investigated in detail in the former Soviet Union and its pharmacological actions have been intensively researched. Pharmacological studies in America have revealed that Deoxypeganine has activity similar to reversibly acting cholinesterase inhibitors. Deoxypeganine inhibits acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase, thereby preventing the degradation of acetylcholine and dopamine. Deoxypeganine is known to cross the blood-brain barrier. (http://www.ethnoleaflets.com/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to yellow powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
86 - 87 C |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|