|
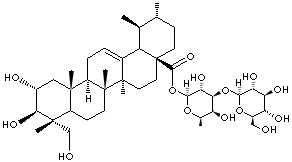
ASIATICOSIDE |
|
Madecassol; (O-alpha-L-Rhamnopyranoxyl-(1-4)-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-6)-O-beta-D- glucopyranosyl)- 2alpha,3beta,23-trihydroxy-12-ursen-28-oat; 2alpha,3beta,23-Trihydroxy-urs- 12-en-28-saeure(O-alpha-L- rhamnopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-6)-O-beta- D-glucopyranosyl)ester; Asiaticosid; Blastoestimulina; Centelase; Dermatologico; Emdecassol; O-6-Desoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-6)-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl 2alpha,3beta,23-trihydroxy-12-ursen-28-at; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
16830-15-2 |
|
EINECS RN |
240-851-7 |
|
FORMULA |
C48H78O19 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
959.12 |
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
Triterpene glycoside |
| CATEGORIES | Extractives and their physically modified derivatives |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
White to off-white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
230 - 233 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
TOXICOLOGICAL |
|
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
|
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. In case of eye contact, flush eyes with water as a precaution. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. In case of skin contact, wash off with soap and plenty of water. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing give artificial respiration. |
|
TARGET ORGANS |
|
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION |
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scartini_scar_cream Centella asiatica (Linn) Urban known as Indian pennywort is a prostate, perennial, faintly aromatic herb found wild throughout India]. Leaves are used as tonic, memory enhancer and also used in the treatment of cataract, eye troubles and in fevers and diarrhea among children. The plant is reported to contain glycosides like brahmosides, indocentelloside, asiaticoside, theankuniside and isotheankuniside. Asiaticoside, a trisaccharide triterpene, has been identified as the most active compound in the plant associated with the healing of wounds and duodenal ulcers, whilst the triterpene saponins are also reported to possess immunomodulatory properties. Asiaticoside is one of the most active compounds which can serve as a marker and is used for its standardization. A few methods such as gravimetric and column chromatography have been suggested for the quantitative estimation of asiaticoside which are not very precise, sensitive and require multiple step extraction and purification. (http://www.science.cmu.ac.th/) Interestingly, asiaticoside was shown to inhibit healing of experimental corneal wounds in rabbits (Callizo et al. 1996). Studies of the effect of asiaticoside in corneal wounds and ulcers have been documented by Abou Shousa & Khalil (1967) and by Mekkawi (1968). Asiaticoside appears also to be able to inhibit collagen production in such a way as to inhibit formation of hypertrophic scars, keloids, and stretch marks (striae gravidarum / striae distensae) (Bosse et al. 1979, Qi et al. 2000, Widgerow et al. 2000, Young & Jewell 2003). Extracts from the plant have been formulated into several commercial products including Collaven™, Emdecassol™, Madecassol™, Centelase™, Marticassol™, Blastoestimulina™, and Trofolastin™. Reports of allergic contact dermatitis, confirmed by patch testing have appeared sporadically following topical use of Madecassol™, (Eun & Lee 1985), Centelase™ (Santucci et al. 1985, Vena & Angelini 1986, Danese et al. 1994), and Blastoestimulina™ (Izu et al. 1992, Aguirre et al. 1993, Bilbao et al. 1995, Gonzalo Garijo et al. 1996). Asiaticoside, asiatic acid, and madecassic acid appear to be the sensitisers (Huriez & Martin 1969, Hausen 1993). The possibility of sensitivity to other components of the formulations (for example, propylene glycol) should not be overlooked (Eun & Lee 1985, Hausen 1993). (http://botanical-dermatology-database.info/) The pharmacological activity of Centella asiatica is thought to be due to several saponin constituents, including asiaticoside, asiatic acid, and madecassic acid. In vitro, each of these compounds stimulated the production of human collagen I, a protein involved in wound healing. Stimulation of collagen synthesis in foreskin fibroblast monolayer cultures by an extract from Herba Centellae has also been reported. Asiaticoside accelerated the healing of superficial postsurgical wounds and ulcers by accelerating cicatricial action. Asiaticoside stimulates the epidermis by activating the cells of the malpighian layer in porcine skin, and by keratinization in vitro. Topical application of asiaticoside promoted wound healing in rats and significantly increased the tensile strength of newly formed skin. Extracts of C. asiatica, and in particular its major triterpene ester glycoside, asiaticoside, are valuable in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Asiaticoside has been reported to decrease fibrosis in wounds, thus preventing new scar formation. The mechanism of action appears to be twofold: by increasing the synthesis of collagen and acidic mucopolysaccharides, and by inhibiting the inflammatory phase of hypertrophic scars and keloids. It has further been proposed that asiaticoside interferes with scar formation by increasing the activity of myofibroblasts and immature collagen. (http://www.zeamais.com/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
White to off-white powder |
| IDENTIFICATION |
pass (TLC) |
|
CONTENT |
80.0% min (Asiaticoside) |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
3.0% max |
| HEAVY METALS |
10ppm
max
|
| Pb |
5ppm max |
| Hg |
0.2ppm max |
| Cd |
0.3ppm max |
| As |
2ppm max |
| ALDRIN |
0,02ppm max |
| SULFATED ASH |
1.0% max |
| PARTICLE SIZE |
100 mesh (95%)x |
| MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTS |
Total bacterial count:
1000CFU/g max Yeast and mold: 100CFU/g max Salmonella: negative E.Coli: negative Staphylococcus: negative |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|