|
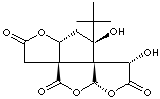
BILOBALIDE |
| Synonyms. (5aR-(3aS',5aalpha,8beta,8aS',9alpha,10aalpha))-9-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-10,10a-dihydro-8,9-dihydroxy- 4H,5aH,9H-furo(2,3-b)furo(3',2':2,3)cyclopenta(1,2-c)furan-2,4,7(3H,8H)-trione; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
33570-04-6 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C15H18O8 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
326.30 |
|
H.S CODE |
2932.29.5050 |
|
SMILES |
C1([C@@]23[C@@]4([C@@](C[C@@H]2OC(C3)=O)(C(C)(C)C)O)[C@H] (O1)OC ([C@@H]4O)=O)=O |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Ginkgolide |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Bioactive main constituent of the terpenoids found in Ginkgo biloba. |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
white to off-white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Soluble in alcohol, DMSO |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Bilobalide PubChem Compound Summary - Bilobalide Drug Bank - Bilobalide KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Bilobalide http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Bilobalide http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Bilobalide http://sydney.edu.au/ http://www.columbia.edu/ Local |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
Not regulated |
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
| PACKING GROUP | |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Not known |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
|
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
|
|
P STATEMENTS |
|
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
36/37/38 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
22-24/25 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |
|
|