|
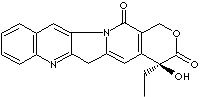
CAMPTOTHECIN |
| Synonyms. Camptothecin; Camptothecine; D-Camptothecin; (S)-Camptothecin; (+)-Camptothecin; (S)-(+)-Camptothecin; 20(S)-Camptothecine; 21,22-Secocamptothecin-21-oic acid lactone; (S)-4-Ethyl-4-hydroxy-1H-pyrano(3',4':6,7)indolizino(1,2-b)quinoline-3,14(4H,12H)-dione; (+)-Camptothecine; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | |
|
CAS RN |
7689-03-4 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C20H16N2O4 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
348.36 |
|
H.S CODE |
2939.99.0000 |
|
SMILES |
c12c(c(n3Cc4c(c3c2)nc2ccccc2c4)=O)COC([C@@]1(CC)O)=O |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antineoplastic, Topoisomerase Inhibitor, Antitumor alkaloid |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
An alkaloid isolated from the stem wood of the Chinese tree, Camptotheca acuminata. This compound selectively inhibits the nuclear enzyme DNA Topoisomerases, Type I. Several semisynthetic analogs of camptothecin have demonstrated antitumor activity. |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
yellowish powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
260 C (Decomposes) |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Insoluble |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetonirile |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
|
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong acids, Strong bases |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2,Flammability:0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This quinoline based alkaloid was found in the bark of the Chinese camptotheca tree. Camptotheca goes by many names in China, including "happy tree", "dragon tree" and "fine tree".Chinese have used the "happy tree" in traditional medicine for thousands of years. It has been used for psoriasis, leukemia and diseases of liver, gallbladder, spleen, and stomach. During the last half century, scientists have discovered its potential as a selective anticancer drug. The unique mode of action for this potent cytotoxic compound was found to act via inhibition of an enzyme known as DNA topoisomerase I. (http://www.scripps.edu/) Camptothecin is an anti-cancer monoterpene indole alkaloid. The gene encoding 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(E)-butenyl 4-diphosphate reductase (designated as CaHDR), the last catalytic enzyme of the MEP pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis, was isolated from camptothecin-producing Camptotheca acuminata. The full-length cDNA of CaHDR was 1686 bp encoding 459 amino acids. Comparison of the cDNA and genomic DNA of CaHDR revealed that there was no intron in genomic CaHDR. Southern blot analysis indicated that CaHDR belonged to a low-copy gene family. RT-PCR analysis revealed that CaHDR expressed constitutively in all tested plant organs with the highest expression level in flowers, and the expression of CaHDR could be induced by 100 ¥ìM methyl-jasmonate (MeJA), but not by 100 mg/L salicylic acid (SA) in the callus of C. acuminata. The complementation of CaHDR in Escherichia coli ispH mutant MG1655 demonstrated its function. [BMB reports 2008; 41(2): 112-118] (http://www.jbmb.or.kr/) Camptothecin derivatives are clinically used antitumor alkaloids that belong to monoterpenoid indole alkaloids. In this study, we investigated the biosynthetic pathway of camptothecin from [1-13C]glucose (Glc) by in silico and in vivo studies. The in silico study measured the incorporation of Glc into alkaloids using the Atomic Reconstruction of Metabolism software and predicted the labeling patterns of successive metabolites from [1-13C]Glc. The in vivo study followed incorporation of [1-13C]Glc into camptothecin with hairy roots of Ophiorrhiza pumila by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The 13C-labeling pattern of camptothecin isolated from the hairy roots clearly showed that the monoterpene-secologanin moiety was synthesized via the 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway, not via the mevalonate pathway. This conclusion was supported by differential inhibition of camptothecin accumulation by the pathway-specific inhibitors (fosmidomycin and lovastatin). The quinoline moiety from tryptophan was also labeled as predicted by the Atomic Reconstruction of Metabolism program via the shikimate pathway. These results indicate that camptothecin is formed by the combination of the 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway and the shikimate pathway. This study provides the innovative example for how a computer-aided comprehensive metabolic analysis will refine the experimental design to obtain more precise biological information. (http://www.plantphysiol.org/)
Topoisomerase inhibitor is a substance that blocks topoisomerases (enzymes that break and rejoin DNA strands and are needed for cells to divide and grow). Blocking these enzymes may kill cancer cells. Certain topoisomerase inhibitors are being studied in the treatment of cancer.
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
yellowish crystalline powder |
| ASSAY | 95.0~103.0% (HPLC) |
|
TOTAL ASH |
0.3% max |
| SPECIFIC ROTATION | +37.0° ~ +42.0 (c=0.4 chloroform:methanol= 8:2) |
|
RELATED SUBSTANCES |
2.0% max (total impurity) |
| MELTING POINT |
259
~ 263 C
|
| PARTICLE SIZE |
100 mesh |
| LOSS ON DRYING | 3.0% max |
| MICROBIOLOGICAL TEST |
Total plate count:1000cfu/g max |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION | |
|
UN NO. |
1544 |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1 |
| PACKING GROUP | III |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION |
|
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Toxic if swallowed. |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Danger |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H301 |
|
P STATEMENTS |
P301 + P310 |
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
25 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-36/37/39-45 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|