|
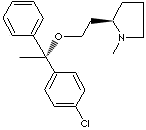
CLEMASTINE FUMARATE |
| (2R)-2-(2-((1R)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenylethoxy)ethyl)-1-methylpyrrolidine (E)-but-2-enedioic acid; (R-(R',R'))-2-(2-(1-(p-Chlorophenyl)-1-phenylethoxy)ethyl)-1-methylpyrrolidinium hydrogen fumarate; (+)-2-(2-((p-Chloro-alpha-methyl-alpha-phenylbenzyl)oxy)ethyl)-1-methyl pyrrolidine fumarate; (+)-(2R)-2-(2-(((R)-p-Chloro-alpha-methyl-alpha-phenylbenzyl)oxy)ethyl)-1-methylpyrrolidine fumarate; Clemastine hydrogen fumarate; Agasten; Aloginan; Alphamin; Anhistan; Clemanil; Fulumino; Inbestan; Kinotomin; Lacretin; Lecasol; Maikohis; Mallermin-F; Marsthine; Masletine; Meclastine hydrogen fumarate; Mecloprodine; Piloral; Reconin; Tavegil; Tavegyl; Tavist; Tavist-1; Telgin-G; Trabest; Xolamin; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
15686-51-8 (parent), 14976-57-9 (fumarate) |
|
EINECS RN |
239-055-2 |
|
FORMULA |
C21H26ClNO·C4H4O4 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
459.96 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
slightly |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon monoxide, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen oxides, Hydrogen chloride |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Avoid contact and inhalation. Target organs: Central nervous system. |
|
EYE |
May cause skin irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through the skin. Eye Contact: May cause eye irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. Material may be irritating to mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. |
|
TARGET ORGANS |
Central nervous system. |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
|
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Histamine is a substance produced by the body as part of
its defence mechanisms. It is stored in cells called mast cells, in almost all
tissues of the body. When the body reacts to a foreign substance (known as an
allergen, eg flower pollen, pet fur, dust mites), the mast cells are stimulated
by the allergen and release their stores of histamine. The released histamine
then binds to its receptors (H1 receptors), causing a chain reaction that
results in allergic symptoms. It causes an increase in blood flow to the area of
the allergy, and the release of other chemicals that add to the allergic
response. All
this results in the symptoms of an allergic reaction. In hayfever, this causes
inflammation of the nose, eyes, skin or airways and results in itchy watery
eyes, a runny nose, sneezing and nasal congestion. Histamine is also responsible
for the symptoms of allergic and itchy rashes, and allergic reactions to foods,
medicines or insect bites. It can also cause more severe allergic reactions such
as angioneurotic oedema, which involves severe swelling of the eyes, lips,
tongue or throat. Clemastine works by blocking histamine H1 receptors. It
doesn't prevent the actual release of histamine from mast cells, but prevents it
binding to its receptors. This in turn prevents the release of other allergy
chemicals and increased blood supply to the area, and provides relief from the
symptoms of allergies. Clemastine is called a sedating antihistamine because it
enters the brain in significant quantities and causes drowsiness. (http://netdoctor.co.uk/) Corticosteroids are the most effective medications for the systemic therapy of allergic dermatitis. They are, however, the most likely to result in unwanted side-effects. Oral prednisolone or prednisone can be administered at 1mg/kg daily in the morning until the symptoms are controlled and then only on alternate days at a reducing dose. Controlling concurrent precipitating and secondary skin disease (acariosis, pyoderma, Malassezia dermatitis, flea infestation) are essential. The use of antihistamines either on their own or with glucocorticoids is recommended – if only to lower the dose of the glucocorticoids. H1 blockers such as chlorpheniramine, clemastine, hydroxyzine, diphenhydramine and trimeprazine have been found to allow for a reduce corticosteroid dosage and may be effective on their own. ( http://www.vetpath.co.za/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline powder |
|
IDENTIFICATION |
pass Test A (TLC), B (Infrared Absorption) |
|
ASSAY |
98.0 - 101.0% |
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
+15° ~ +18 ° |
|
HEAVY METALS |
20ppm max |
|
LOS ON DRYING |
0.5% max |
|
RELATED SUBSTANCES |
1.0% max (total), 0.3% max (individual) |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|
|
|
| PRICE |
| U$6,900 (500g) |