|
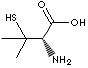
D-PENICILLAMINE |
| (2S)-2-amino-3-methyl-3-sulphanylbutanoic acid; (D)-Penicillamine; (-)-Penicillamine; (2S)-2-Amino-3-methyl-3-sulfanylbutanoic acid; (S)-3,3-Dimethylcysteine; (S)-Penicillamin; (S)-Penicillamine; 2-Amino-3-mercapto-3-methylbutanoic acid; 3-Mercapto-D-valine; Artamine; Cuprenil; Cuprimine; Cupripen; D-(-)-Penicillamine; D-3-Mercaptovaline; D-Mercaptovaline; D-Penamine; Depamine; Kuprenil; Mercaptovaline; Mercaptyl; Metalcaptase; Pendramine; Penicilamina; Penicillamin; Penicillamina; Penicillamine; Penicillaminum; Trolovol; beta-Thiovaline; alpha-Amino-beta-methyl-beta-mercaptobutyric acid; beta,beta-Dimethylcysteine; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
52-67-5 |
|
EINECS RN |
200-148-8 |
|
FORMULA |
|
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
|
|
CHEMICAL FAMILY |
alpha-Amino acid |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
202 - 206 C (decomposes) |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Freely soluble (slightly soluble in alcohol; insoluble in chloroform, in ether, in acetone, in benzene, and in carbon tetrachloride) |
|
pH |
4.5 - 5.5 (1% aqueous solution) |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
NOx, SOx |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Will not occur. |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2. Flammability: 1, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
May cause irritation. Remove to fresh air. |
|
EYE |
May cause irritation. Flush with copious quantities of water. |
|
SKIN |
May cause irritation. Flush with copious quantities of water. This material may be absorbed through skin. |
|
INGESTION |
May cause irritation and a slightly bitter taste. Flush out mouth with water. This material is readily but incompletely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. Causes respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XN |
|
RISK PHRASES |
63 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
22-36/37/39-45 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Penicillamine Penicillamine is an antirheumatic drug used to treat patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. It also is classified as a metal binding (chelating) agent used for treating Wilson's disease, a genetic disease that causes excessive copper to accumulate in the body. The mechanism of action of penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis is unknown but it may be related to reduction of collagen formation. (Collagen is a type of tissue that forms a part of scar tissue that results from inflammation) and suppression of the immune system. In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, penicillamine appears to slow the progression of the disease (specifically deformities of the joints) and improve function. For this reason it is considered a disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD). Penicillamine binds copper, iron, mercury, lead, and cystine which then are excreted in the urine, and this mechanism is important in treating several nonrheumatic diseases including Wilson's disease. The FDA approved penicillamine in December 1970. (http://www.medicinenet.com/) D-penicillamine is a degradation product of penicillin. Only the d-isomer is used because l-isomer causes optic neuritis. It is slowly but adequately absorbed after oral administration. The drug gets metabolised in the body and is excreted in the urine and faeces. D-penicillamine is used in severe and active rheumatoid arthritis, it is used mainly as chelating agent in heavy metal poisoning as in lead, mercury and copper poisoning. It is used in Wilson's disease. (http://www.webhealthcentre.com/) D-Penicillamine, usually referred to as penicillamine, (brand name D-Penamine) is a medicine used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Occasionally it is used to treat other rheumatic diseases such as systemic sclerosis. Penicillamine should not be confused with the antibiotic penicillin, which is a different compound. Those who are allergic to penicillin may not necessarily be sensitive to penicillamine. While penicillamine can be very effective for some patients, it is used infrequently today as more effective medicines have become available. Penicillamine is an immunosuppressive medicine, which means that it works by reducing the activity of the immune system. (http://www.rheumatology.org.au/) Therapeutic Classification:
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white to almost white, crystalline powder |
| IDENTIFICATION |
Pass tests (Optical Rotation, HPLC, TLC, Phosphotungstic acip darf) |
|
ASSAY |
97.0 % - 102.0 % (HPLC) |
|
pH |
4.5 - 5.5 (1% aqueous solution) |
| OPTICAL ROTATION | -61.0° ~ -65.0° |
| PEN DISULPHIDE |
1.0% max |
| PENICILLIN |
0,1ppm max |
|
ASH |
0.1% max |
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
| LOSS ON DRYING | 0.5% max |
|
|
| PRICE |