|
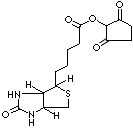
N-HYDROXYSUCCINIMIDOBIOTIN |
|
Biotinyl-N-Hydroxysuccinimide ester; BNHS, NHS-D-Biotin; N-Succinimide-D-Biotinate; Biotinyl-N-hydroxy-succinimide; Biotin O-Su; (2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)5-(2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a- hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-6-yl)pentanoate; 1-((5-(2-Oxohexahydro-1H-thieno(3,4-d) imidazol-4-yl)pentanoyl)oxy)-2,5-pyrrolidinedione; Biotin-NHS; Biotin-OSu; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
35013-72-0 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C14H19N3O5S |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
341.38 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
White to off-white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
212 C |
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents. |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides. nitrogen oxides, Sulphur oxides. |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 0 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Causes irritation. Avoid contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. |
|
EYE |
May cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
22-24/25 |
|
|
| OTHER INFORMATION |
|
|
Proteomic approaches require simple and efficient protein purification
methodologies that are amenable to high throughput. Biotinylation is an
attractive approach for protein complex purification due to the very high
affinity of avidin/streptavidin for biotinylated templates. Here, we describe an
approach for the single-step purification of transcription factor complex(es)
based on specific in vivo biotinylation. (http://www.pnas.org/)
Biotinylation is a rapid method of detecting nucleic acids for use in a Western blot. Biotin is covalently coupled to primary amines of immunoglobin. Biotinylation of antigens is used to improve immunoassays. Proteins can be biotinylated in 1 hour. CHO B2 cells transfected with alpha5 were washed with buffer and biotinylated for 60 minutes. After washing, the cells were extracted with protease inhibitors for 30 minutes, and centrifuged for 10 minutes. (http://student.biology.arizona.edu/) Biotinylation of a protein generally involves chemical modification of a translated protein. Using this methodology, however, biotinylation at a specific position remains difficult. We investigated whether it would be possible to use an Escherichia coli initiator tRNAfmet aminoacylated with methionine biotinylated at the .ALPHA.-amino group to introduce a biotin tag specifically at the N terminus. We report here that a biotin tag could be incorporated into the green fluorescent protein (GFP) at the N-terminal site, in the presence of an E. coli initiator tRNAfmet aminoacylated with methionine biotinylated at the .ALPHA.-amino group. The biotinylated GFP was purified by simple monomeric streptavidin-agarose affinity column chromatography. Based on the total amount of GFP molecules, the purification yield and the biotin labelling efficiency of this system were approximately 7% and 10-20%, respectively, according to the densitometric analysis of Western blots. Judging from the results of a fluorescence imaging experiment, almost all the purified GFP molecules retained the native fluorescence activity. Importantly, the present results support the hypothesis that the E. coli initiator tRNAfmet aminoacylated with a relatively large substituent can be recognized by an E. coli ribosome and adequately placed at the P site to initiate translation. (http://sciencelinks.jp/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
White to off-white powder |
| PURITY |
99.0% min |
|
|
| PRICE INFORMATION |