|
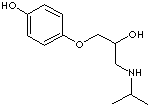
O-DESMETHYLMETOPROLOL |
| 4-(2-Hydroxy-3-((1-methylethyl)amino)propoxy)benzeneethanol; 1-(4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)phenoxy)-3- (propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol; 4-(2-Hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)phenylethyl Alcohol; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
62572-94-5 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C14H23NO3 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
253.34 |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
off-white powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
|
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents, Water |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides, silicon oxides |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Will not occur. |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2. Flammability: 1, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Combustible Liquid, Irritant |
|
EYE |
Causes eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
May be harmful if absorbed through skin. Causes skin irritation. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. Causes respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD SYMBOL |
XI |
|
RISK PHRASES |
38 |
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-36 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metoprolol Metoprolol, first introduced in 1975, is one of a class of drugs known as beta-blockers. Beta-blockers are widely prescribed to treat disorders of the heart and circulation. They work by blocking the action of adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) - two chemicals produced by the body that increase heart rate and raise blood pressure. Cardioselective beta-blockers are especially effective at slowing heart rate and reducing the force of the heartbeat, thereby reducing the workload of the heart. These actions make beta-blockers, including metoprolol, particularly effective in the treatment of a range of cardiovascular problems. Metoprolol can be prescribed for: high blood pressure, angina (the condition caused by narrowing of the arteries and reduction in the amount of oxygen-carrying blood reaching the heart), patients who have had a heart attack, heart failure (a condition arising from weakening of the heart muscle which makes the heart pump less efficiently), certain disturbances of cardiac rhythm (arrhythmias), disorders of the function of the heart involving palpitations. (http://www.ctsu.ox.ac.uk/) O-Demethylmetoprolol is a pharmacologically active urinary metoprolol metabolite 5 to 10X less potent than metoprolol. |
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
Clear liquid |
|
PURITY |
98.0% min (GC) |
|
|
| PRICE |