|
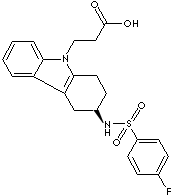
RAMATROBAN |
| (+)-(3R)-3-(p-Fluorobenzenesulfonamido)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrocarbazole-9-propionic acid; 3-(4-Fluorophenylsulfonamido)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9-carbazole propanoic acid; Baynas; (R)-3-(((4-Fluorophenyl)sulfonyl)amino)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-carbazole-9-propanoic acid; |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|
|
CAS RN |
116649-85-5 |
|
EINECS RN |
|
|
FORMULA |
C21H21FN2O4S |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
416.47 |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Antiplatelet |
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystalline powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Insoluble (soluble in DMSO) |
|
pH |
|
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong acids, Strong bases |
| DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS |
Carbon oxides. Nitrogen oxides. |
| POLYMERIZATION | Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2, Flammability: 0, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| SAFETY |
|
|
HAZARD NOTES |
Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. |
|
EYE |
Cause eye irritation. |
|
SKIN |
Cause skin irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through the skin. |
|
INGESTION |
May be harmful if swallowed. Material is irritating to mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. |
|
INHALATION |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. |
|
CHRONIC |
|
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION |
|
|
UN NO. |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| PACKING GROUP |
|
| HAZARD CODE |
XI |
|
RISK STATEMENTS |
36/37/38 |
|
SAFETY STATEMENTS |
26-36/37/39-45 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL INFORMATION | |
|
It is known that thromboxane A2 (TXA2) contributes to
various diseases such as bronchial asthma, ischemic heart disease,
cerebrovascular disorders and allergic rhinitis. A number of TXA2
synthase inhibitors and TXA2 receptor (TP receptor) antagonists have
been developed to treat these diseases. Ramatroban (BAY u 3405) was developed as
a potent TP receptor antagonist with excellent efficacy against allergic
rhinitis in many animal models and patients. Recent studies also revealed that
ramatroban can block the newly identified PGD2 receptor,
chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells (CRTh2).
PGD2 induces migration and degranulation of eosinophils through CRTh2
and contributes to late-phase inflammation and cell damage. Accordingly, it was
considered that ramatroban suppresses the late-phase inflammation via TP
receptor and CRTh2 blockade. In tenns of the efficacy on vascular systems, it
was revealed that ramatroban can suppress the expression of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and adhesion molecules in endothelial cells
and prevent exacerbation of inflammation by blocking these responses. According
to our recent studies in hypercholesterolemic rabbits ramatroban prevents
macrophage infiltration through MCP-1 downregulation and neointimal formation
after balloon injury and attenuates vascular response to acetylcholine.
Therefore, ramatroban may be beneficial in the treatment of atherosclerosis.
(http://cat.inist.fr/) Antiplatelet drugs are a group of powerful medications that prevent the formation of blood clots. When you are wounded, platelets arrive on the scene and group together, forming a blood clot that stops the bleeding. In many situations, this is a good thing. But platelets can also aggregate when injury to a blood vessel occurs, like during atherosclerosis. In this situation, the platelets cause blood clots to develop in an already stressed artery. Antiplatelet medications can prevent this process from occurring. Aspirin is the most common antiplatelet drug. Other antiplatelet drugs used to treat heart disease include Plavix (clopidogrel bisulfate) and Ticlid (ticlopidine hydrochloride). (http://my.clevelandclinic.org/)
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
|
| PRICE |
|
U$2,500 (5g) |